Sustainable Development Goals
Targets and Indicators with Data Availability
Note: The data may be updated periodically as more information become available.
 |
Eradicate Extreme Poverty
By 2030, eradicate extreme poverty for all people everywhere, currently measured as people living on less than $1.25 a day.
|
Indicator 1.1.1 | Proportion of the population living below the international poverty line by sex, age, employment status and geographic location (urban/rural)
|
Singapore does not use international and national poverty lines as the poverty lines may not fully reflect the complexity of issues faced by those who need help. Instead, Singapore adopts a more flexible approach by providing multiple lines of assistance with different eligibility criteria, which allows us to tailor our assistance to the needs of different groups.
|
 |
 |
Reduce Poverty by At Least 50%
By 2030, reduce at least by half the proportion of men, women and children of all ages living in poverty in all its dimensions.
|
Indicator 1.2.1 | Proportion of population living below the national poverty line, by sex and age
|
Singapore does not use international and national poverty lines as the poverty lines may not fully reflect the complexity of issues faced by those who need help. Instead, Singapore adopts a more flexible approach by providing multiple lines of assistance with different eligibility criteria, which allows us to tailor our assistance to the needs of different groups.
|
 |
Indicator 1.2.2 | Proportion of men, women and children of all ages living in poverty in all its dimensions according to national definitions
|
Singapore does not use international and national poverty lines as the poverty lines may not fully reflect the complexity of issues faced by those who need help. Instead, Singapore adopts a more flexible approach by providing multiple lines of assistance with different eligibility criteria, which allows us to tailor our assistance to the needs of different groups.
|
 |
Implement social protection systems
Implement nationally appropriate social protection systems and measures for all, including floors, and by 2030 achieve substantial coverage of the poor and the vulnerable.
|
Indicator 1.3.1 | Proportion of population covered by social protection floors/systems, by sex, distinguishing children, unemployed persons, older persons, persons with disabilities, pregnant women, newborns, work-injury victims and the poor and the vulnerable
|
(e) Proportion of unemployed persons receiving unemployed cash benefit, by sex
All Singaporeans have access to the Central Provident Fund scheme. Singaporeans who meet specified criteria may also be eligible for support schemes such as ComCare and the SkillsFuture Jobseeker Support scheme.
|
 |
Equal Rights to Ownership, Basic Services, Technology and Economic Resources
By 2030, ensure that all men and women, in particular the poor and the vulnerable, have equal rights to economic resources, as well as access to basic services, ownership and control over land and other forms of property, inheritance, natural resources, appropriate new technology and financial services, including microfinance.
|
Indicator 1.4.1 | Proportion of population living in households with access to basic services
Indicator 1.4.2 | Proportion of total adult population with secure tenure rights to land, (a) with legally recognized documentation, and (b) who perceive their rights to land as secure, by sex and type of tenure
|
Proportion of total adult population with land ownership that have secure rights over the land (regardless of use of land) is 100%.
|
 |
 |
Build Resilience to Environmental, Economic and Social Disasters
By 2030, build the resilience of the poor and those in vulnerable situations and reduce their exposure and vulnerability to climate-related extreme events and other economic, social and environmental shocks and disasters.
|
Indicator 1.5.1 | Number of deaths, missing persons and directly affected persons attributed to disasters per 100,000 population
|
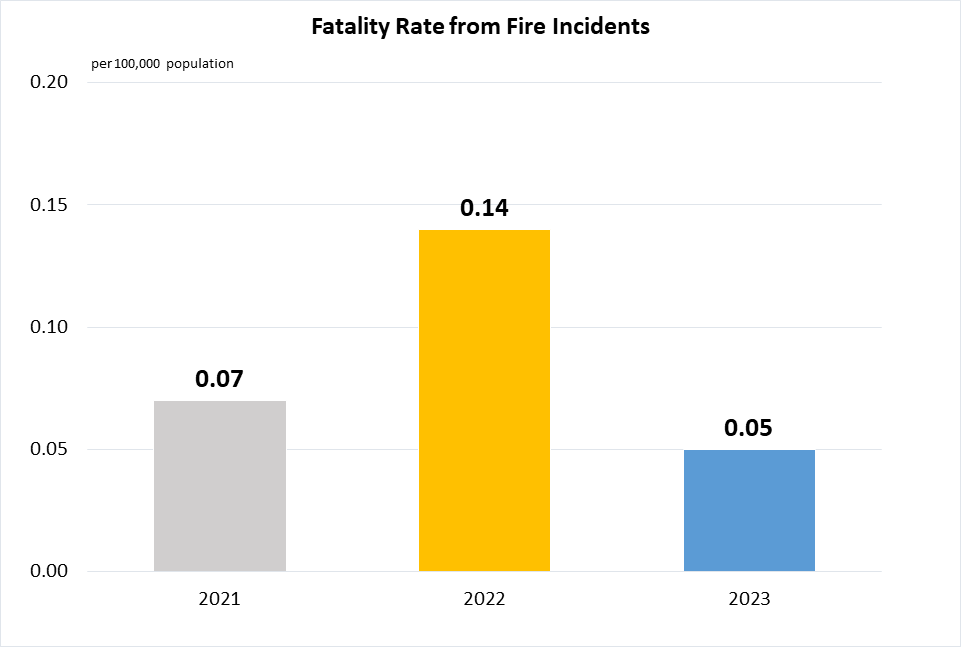
Singapore is not prone to natural disasters.
|
 |
Indicator 1.5.2 | Direct economic loss attributed to disasters in relation to global gross domestic product (GDP)
|
Singapore is not prone to natural disasters, and hence data on direct economic loss attributed to natural disasters is nil or negligible.
|
Indicator 1.5.3 | Number of countries that adopt and implement national disaster risk reduction strategies in line with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030
|
As a city state, Singapore’s government carries out both national and local functions. Singapore is not prone to natural disasters and therefore does not systematically follow the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030. Nevertheless, in areas covered by the Sendai Framework, we have invested in and implemented strategies such as fire safety regulations, public warning systems, community engagement and the use of technology to prevent disasters and risks and improve emergency response.
|
 |
Indicator 1.5.4 | Proportion of local governments that adopt and implement local disaster risk reduction strategies in line with national disaster risk reduction strategies
|
As a city state, Singapore’s government carries out both national and local functions. Singapore is not prone to natural disasters and therefore does not systematically follow the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030. Nevertheless, in areas covered by the Sendai Framework, we have invested in and implemented strategies such as fire safety regulations, public warning systems, community engagement and the use of technology to prevent disasters and risks and improve emergency response.
|
 |
 |
Mobilize Resources to Implement Policies to End Poverty
Ensure significant mobilization of resources from a variety of sources, including through enhanced development cooperation, in order to provide adequate and predictable means for developing countries, in particular least developed countries, to implement programmes and policies to end poverty in all its dimensions.
|
Indicator 1.A.1 | Total official development assistance grants that focus on poverty reduction as a share of the recipient country’s gross national income
|
Not applicable. Singapore does not receive Official Development Assistance.
|
|
Indicator 1.A.2 | Proportion of total government spending on essential services (education, health and social protection)
|
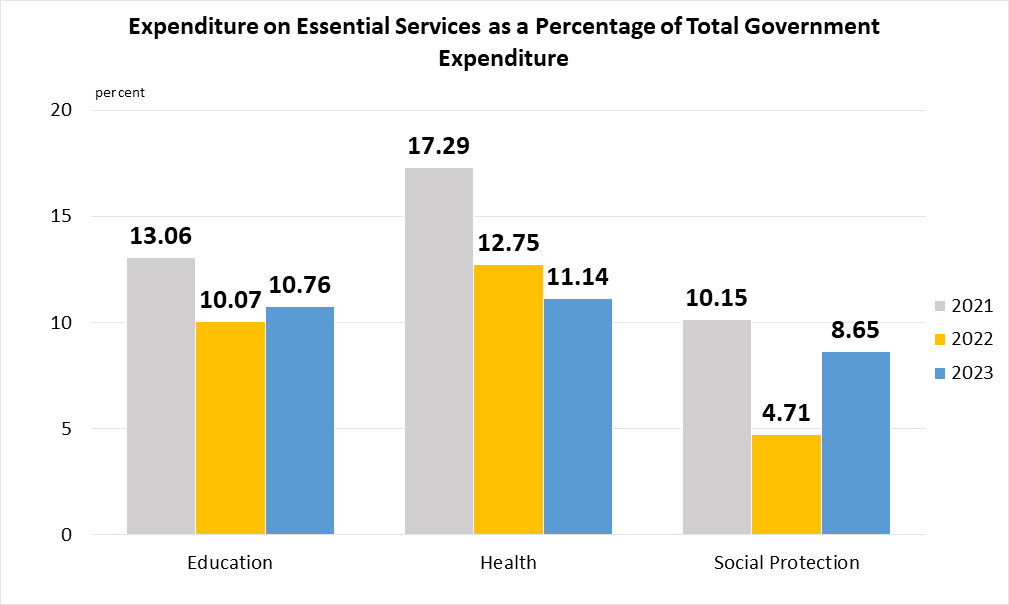
Data are taken from United Nations Global SDG Database.
|
 |
|
 |
Create Pro-Poor and Gender-Sensitive Policy Frameworks
Create sound policy frameworks at the national, regional and international levels, based on pro-poor and gender-sensitive development strategies, to support accelerated investment in poverty eradication actions.
|
Indicator 1.B.1 | Pro-poor public social spending
|
We are reviewing the data to be used to compute this indicator. Singapore’s system of taxes and benefits is fair and progressive, where those with greater needs receive more help. For example, comparing resident households living in the smallest dwelling type (1-2 room public housing flats) with all resident households, the former typically received double the average amount of Government subsidies and transfers per household member. Government subsidies and transfers include substantial broad-based subsidies in key domains (e.g. education, housing, healthcare), as well as targeted subsidies and transfers such as the Ministry of Education’s Financial Assistance Scheme, the Ministry of Health’s Community Health Assist Scheme, and the Ministry of Social and Family Development’s ComCare assistance.
|
|