Sustainable Development Goals
Targets and Indicators with Data Availability
Note: The data may be updated periodically as more information become available.
 |
Reduce Maternal Mortality
By 2030, reduce the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70 per 100,000 live births.
|
Indicator 3.1.1 | Maternal mortality ratio
Indicator 3.1.2 | Proportion of births attended by skilled health personnel
 |
End All Preventable Deaths Under 5 Years of Age
By 2030, end preventable deaths of newborns and children under 5 years of age, with all countries aiming to reduce neonatal mortality to at least as low as 12 per 1,000 live births and under-5 mortality to at least as low as 25 per 1,000 live births.
|
Indicator 3.2.1 | Under-5 mortality rate
|
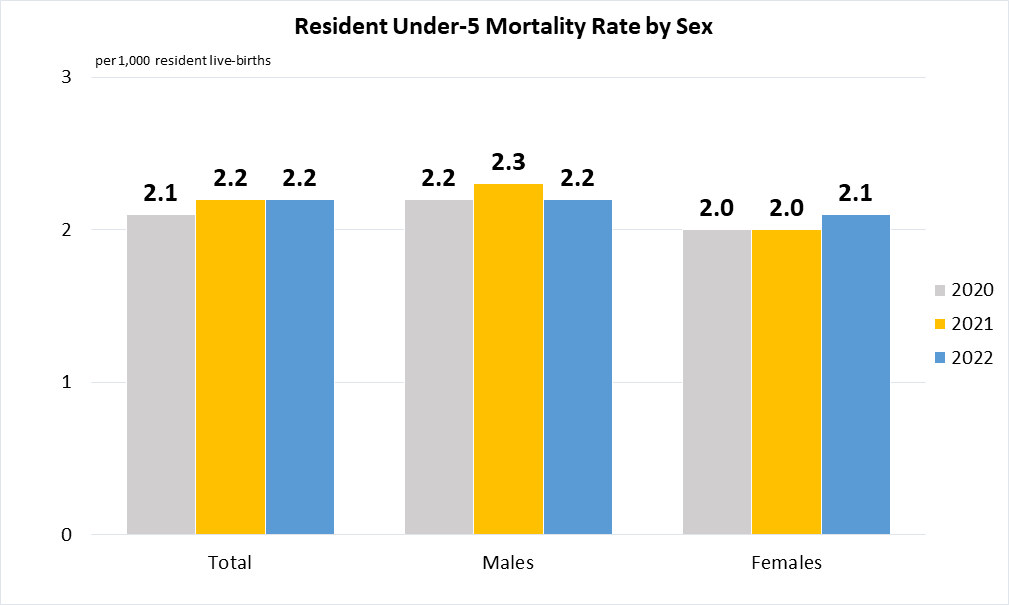
Residents comprise Singapore citizens and permanent residents.
Note: Figure for latest available year is preliminary.
|
 |
Indicator 3.2.2 | Neonatal mortality rate
 |
Fight Communicable Diseases
By 2030, end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and neglected tropical diseases and combat hepatitis, water-borne diseases and other communicable diseases.
|
Indicator 3.3.1 | Number of new HIV infections per 1,000 uninfected population, by sex, age and key populations
|
(a)
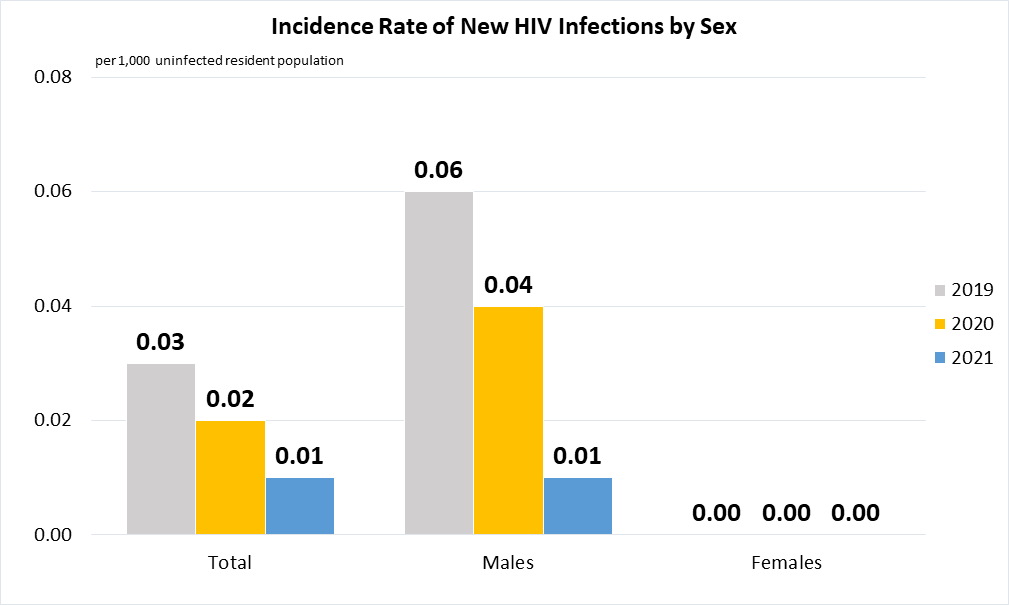
Data are taken from United Nations SDG Global Database. Data refer to the incidence rate of new HIV infections (per 1,000 uninfected resident population i.e. Singapore citizens and permanent residents). The incidence estimation is based on World Health Organisation (WHO) Spectrum with modelling done using notifications received by the National HIV Registry from clinicians and laboratories.
|
 |
Indicator 3.3.2 | Tuberculosis incidence per 100,000 population
|
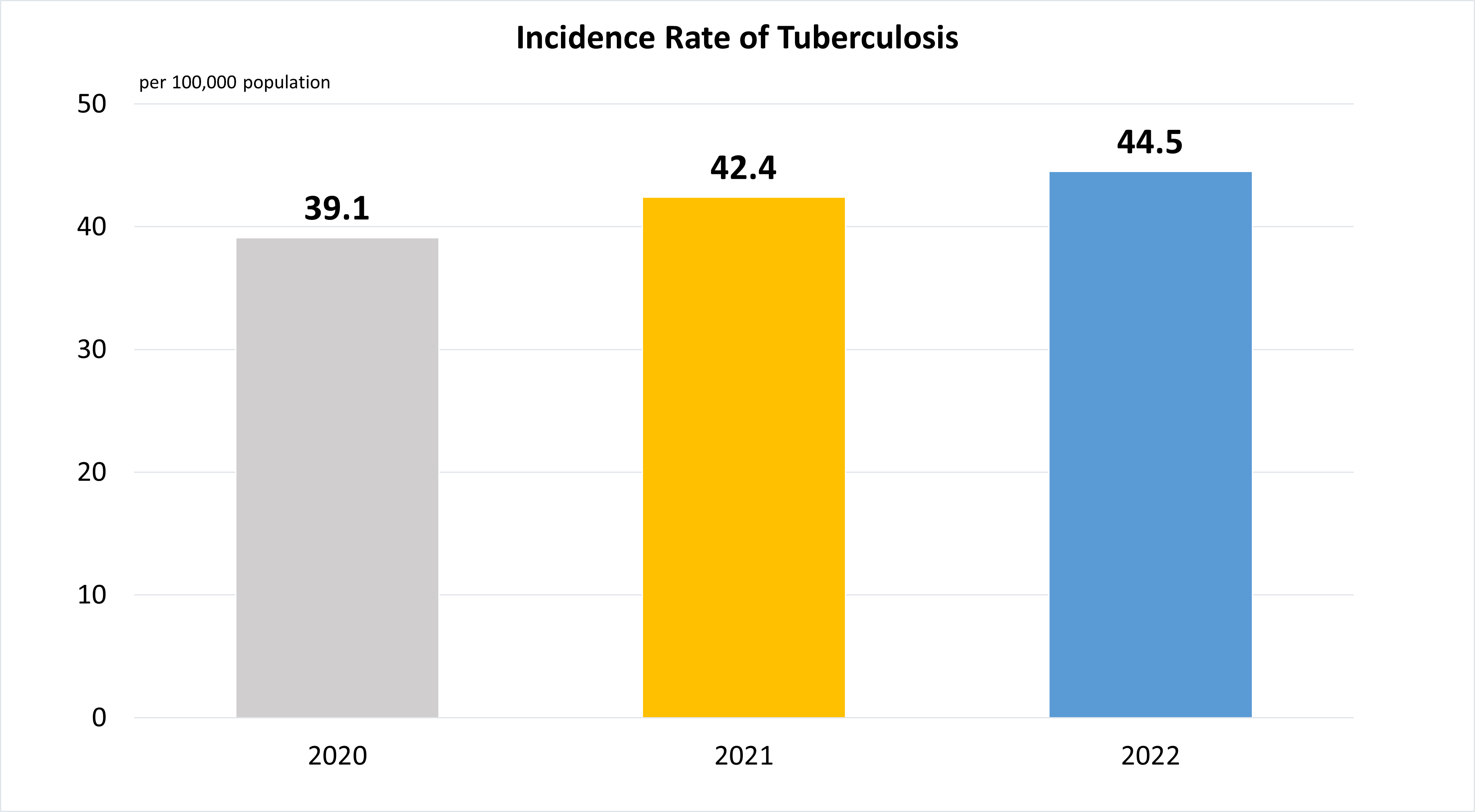
Data refer to incidence rate of new Tuberculosis infections (per 100,000 population) among Singapore residents and long staying foreigners.
|
 |
Indicator 3.3.3 | Malaria incidence per 1,000 population
|
Data for indigenous malaria incidence rate (per 100,000 total population) are nil or negligible since 2010.
|
 |
Indicator 3.3.4 | Hepatitis B incidence per 100,000 population
Indicator 3.3.5 | Number of people requiring interventions against neglected tropical diseases
 |
Reduce Mortality from Non-communicable Diseases and Promote Mental Health
By 2030, reduce by one third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being.
|
Indicator 3.4.1 | Mortality rate attributed to cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes or chronic respiratory disease
|
(a)
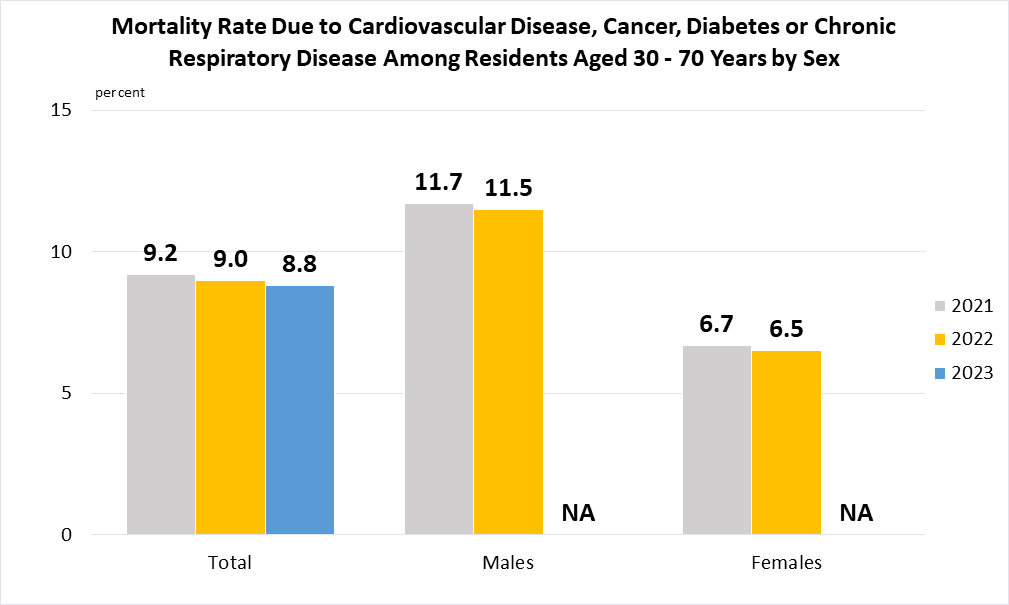
Data pertain to Singapore residents (i.e. Singapore citizens and permanent residents) aged 30 - 70 years and are derived from the Mortality Tabulation List of the International Classification of Diseases - Tenth Revision's ICD10 codes: I00-I99 (Cardio), C00-C97 (Cancer), E10-E14 (Diabetes) and J30-J98 (Chronic Respiratory Disease).
|
 |
Indicator 3.4.2 | Suicide mortality rate
|
(a)
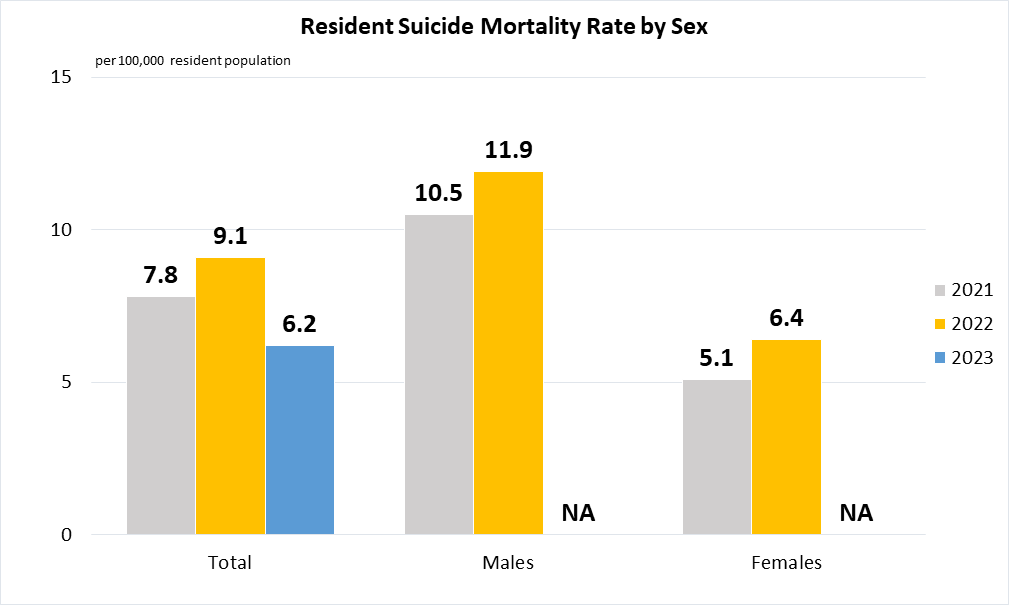
Data pertain to Singapore residents (i.e. Singapore citizens and permanent residents) and are derived from the Mortality Tabulation List of the International Classification of Diseases - Tenth Revision's ICD10 codes X60-X84.
|
|
 |
 |
Prevent and Treat Substance Abuse
Strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance abuse, including narcotic drug abuse and harmful use of alcohol.
|
Indicator 3.5.1 | Coverage of treatment interventions (pharmacological, psychosocial and rehabilitation and aftercare services) for substance use disorders
Indicator 3.5.2 | Alcohol per capita consumption (aged 15 years and older) within a calendar year in litres of pure alcohol
|
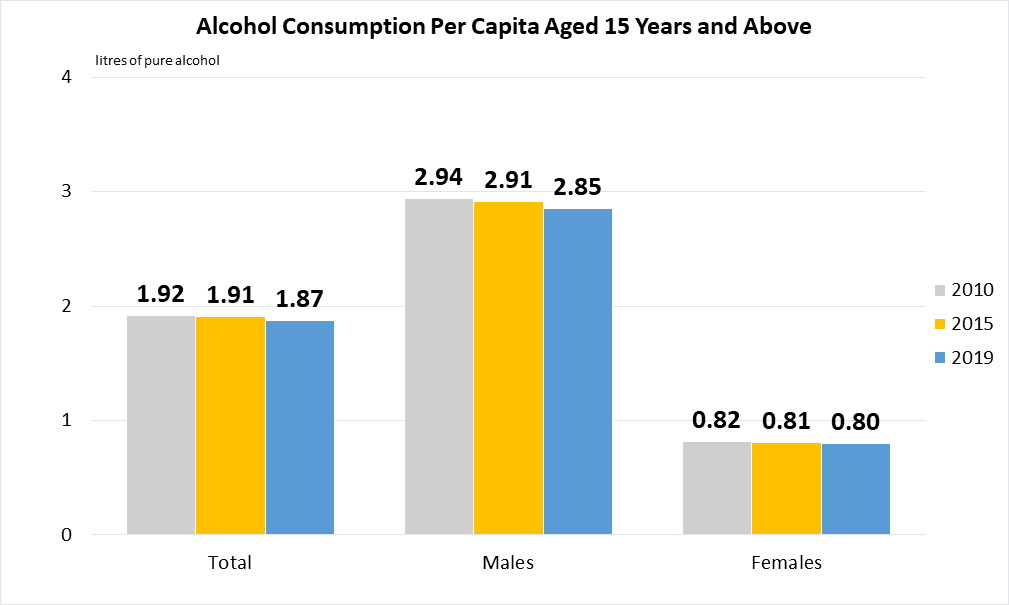
Data are taken from United Nations SDG Global Database.
|
 |
 |
Reduce Road Injuries and Deaths
By 2020, halve the number of global deaths and injuries from road traffic accidents.
|
Indicator 3.6.1 | Death rate due to road traffic injuries
 |
Universal Access to Sexual and Reproductive Care, Family Planning and Education
By 2030, ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health-care services, including for family planning, information and education, and the integration of reproductive health into national strategies and programmes.
|
Indicator 3.7.2 | Adolescent birth rate (aged 10–14 years; aged 15–19 years) per 1,000 women in that age group
|
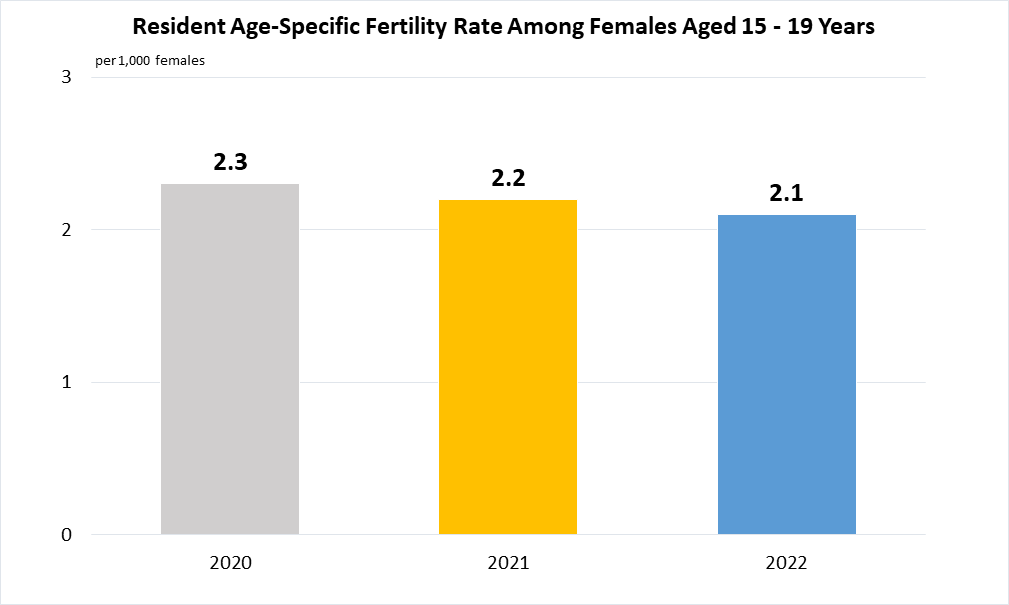
The corresponding data for females aged 10-14 years are nil or negligible.
|
 |
 |
Achieve Universal Health Coverage
Achieve universal health coverage, including financial risk protection, access to quality essential health-care services and access to safe, effective, quality and affordable essential medicines and vaccines for all.
|
Indicator 3.8.1 | Coverage of essential health services
|
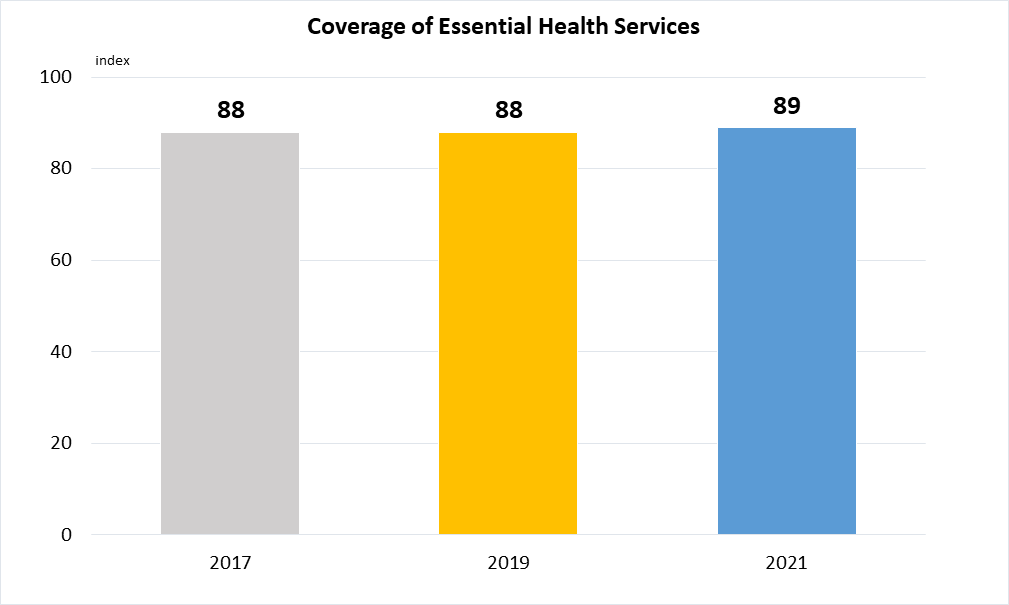
Data are taken from World Health Organisation.
|
|
 |
Indicator 3.8.2 | Proportion of population with large household expenditures on health as a share of total household expenditure or income
|
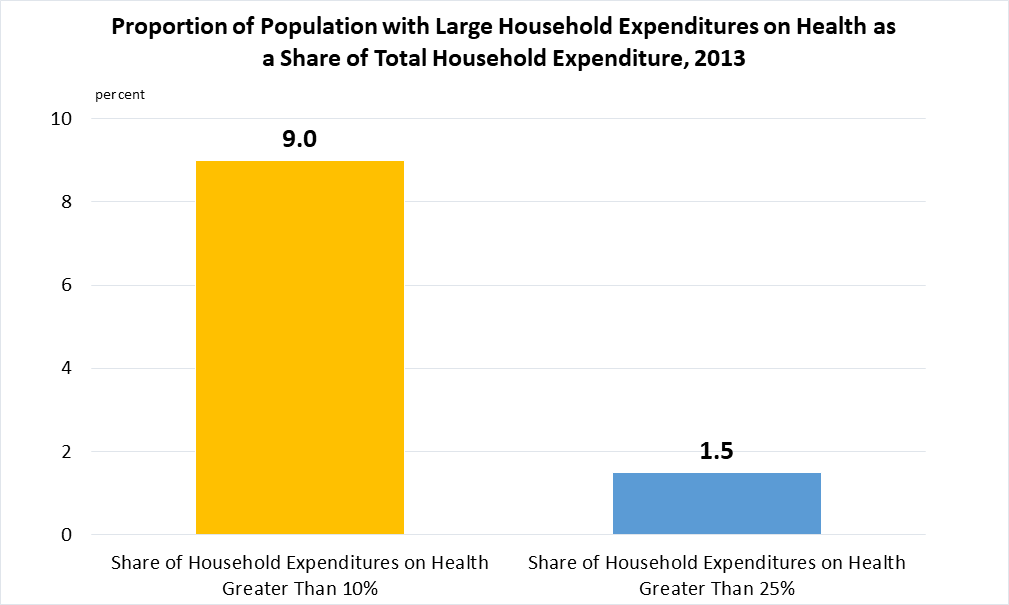
Note: Data are only available for 2013.
|
|
 |
 |
Reduce Illnesses and Death from Hazardous Chemicals and Pollution
By 2030, substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water and soil pollution and contamination.
|
Indicator 3.9.1 | Mortality rate attributed to household and ambient air pollution
|
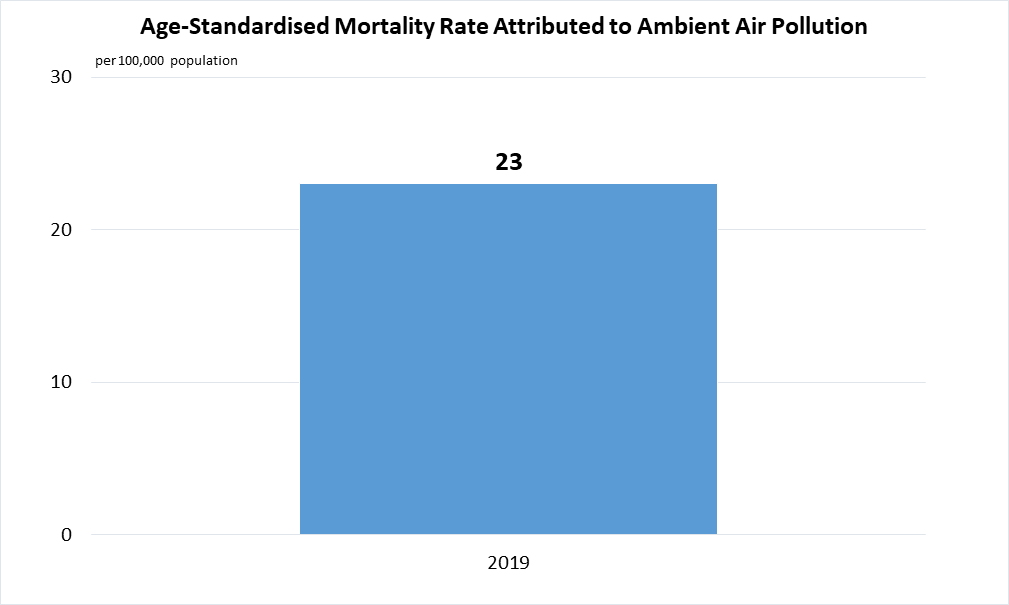
Data are taken from United Nations SDG Global Database.
Data for household air pollution are not available.
|
Indicator 3.9.2 | Mortality rate attributed to unsafe water, unsafe sanitation and lack of hygiene (exposure to unsafe Water, Sanitation and Hygiene for All (WASH) services)
|
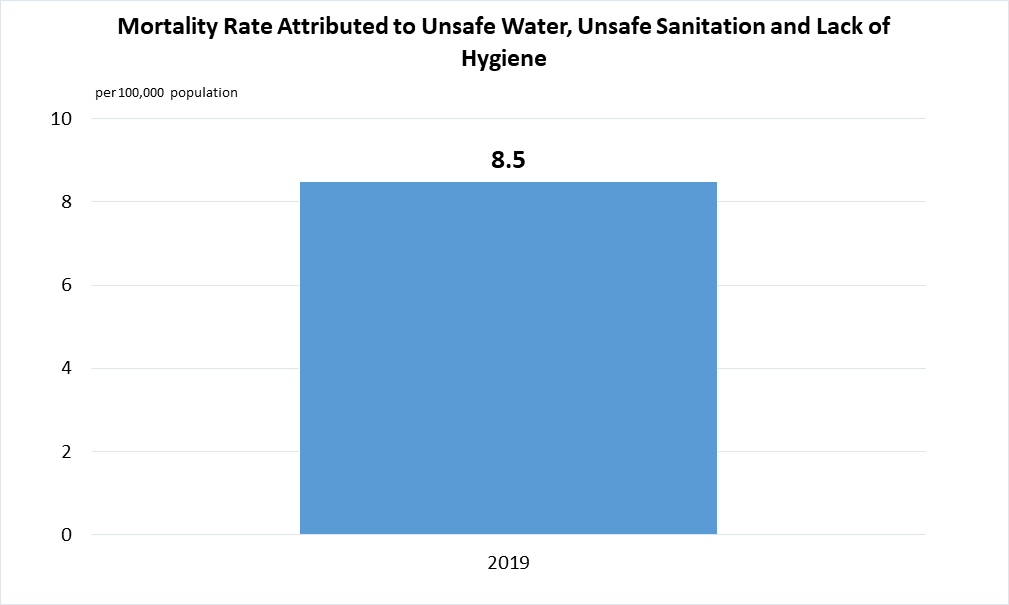
Data are taken from United Nations SDG Global Database.
|
Indicator 3.9.3 | Mortality rate attributed to unintentional poisoning
|
Data are taken from United Nations SDG Global Database.
Data for mortality rate attributed to unintentional poisoning (per 100,000 population) are nil or negligible since 2000 for years where data are available.
|
 |
|
 |
Implement the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control
Strengthen the implementation of the World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control in all countries, as appropriate.
|
Indicator 3.A.1 | Age-standardized prevalence of current tobacco use among persons aged 15 years and older
|
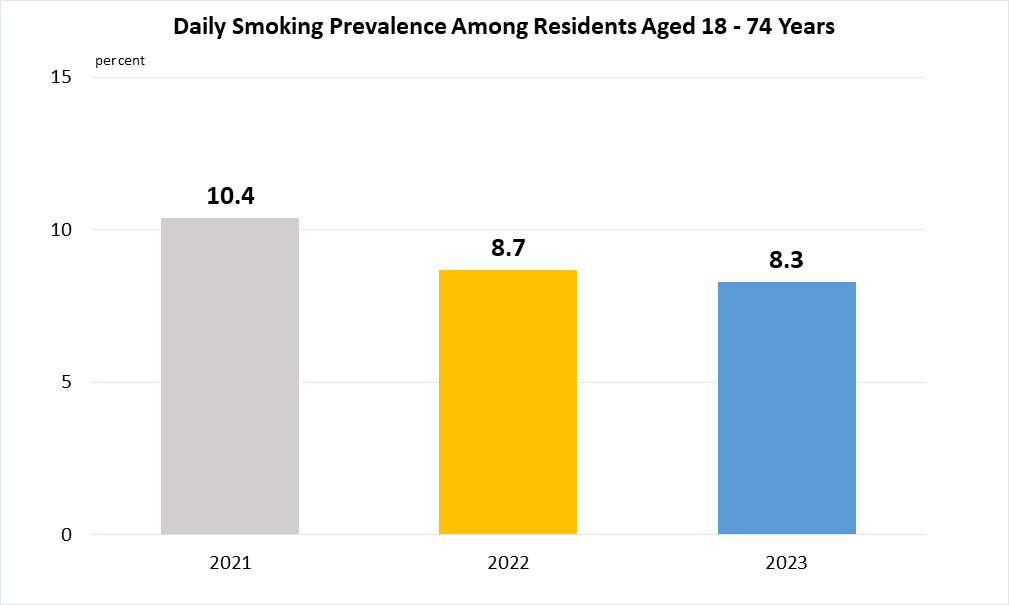
Data refer to the daily smoking prevalence among aged 18 - 74 years for Singapore residents (i.e. Singapore citizens and permanent residents), age-standardised to the World Health Organisation (WHO) World Standard Population.
|
 |
 |
Support Research, Development and Universal Access to Affordable Vaccines and Medicines
Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non-communicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries, provide access to affordable essential medicines and vaccines, in accordance with the Doha Declaration on the TRIPS Agreement and Public Health, which affirms the right of developing countries to use to the full the provisions in the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights regarding flexibilities to protect public health, and, in particular, provide access to medicines for all.
|
Indicator 3.B.1 | Proportion of the target population covered by all vaccines included in their national programme
|
(a)
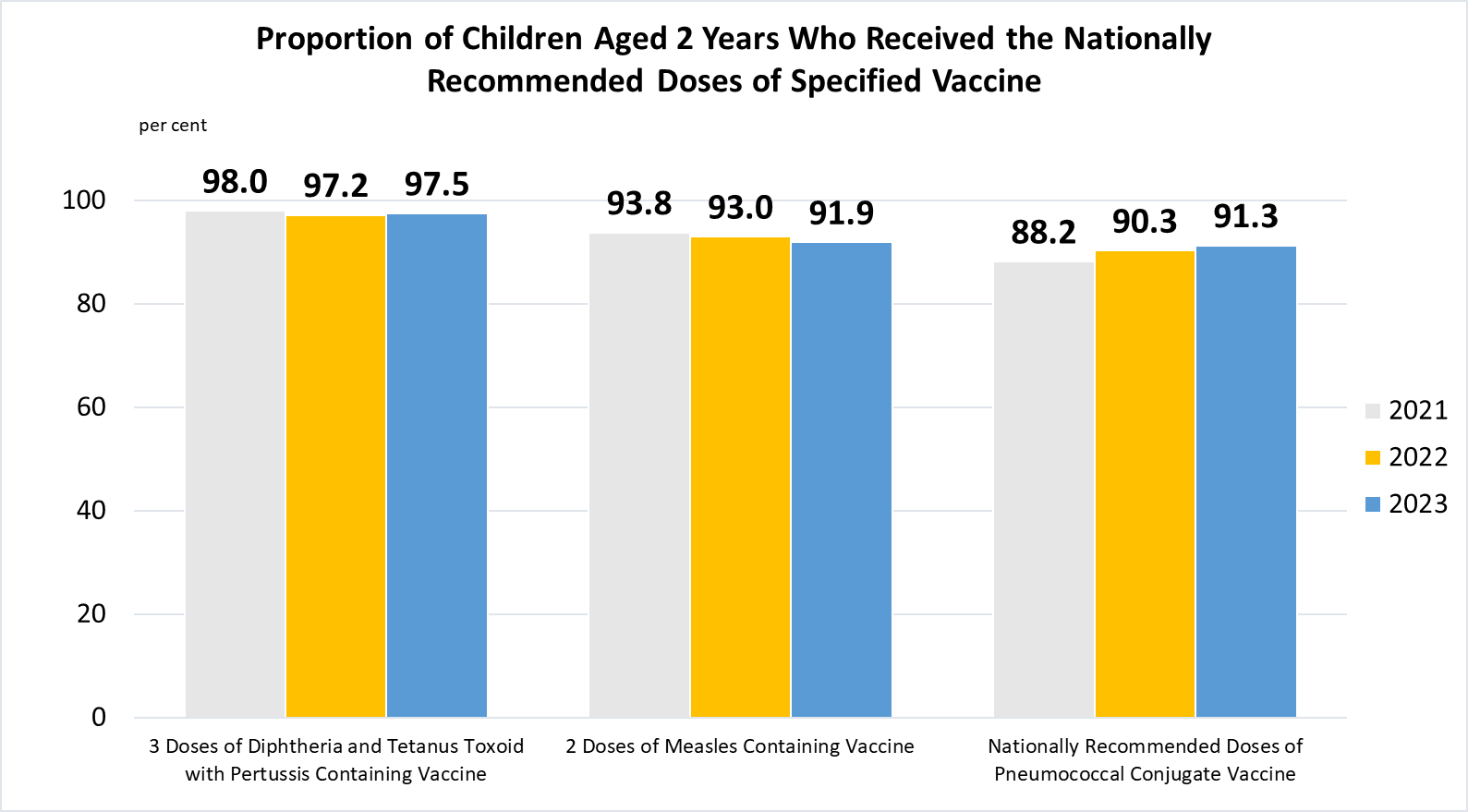
Data are based on Singapore residents (i.e. Singapore citizens and permanent residents) in the respective 2-year old birth cohort (e.g. data for 2023 refer to those born in 2021).
(b)
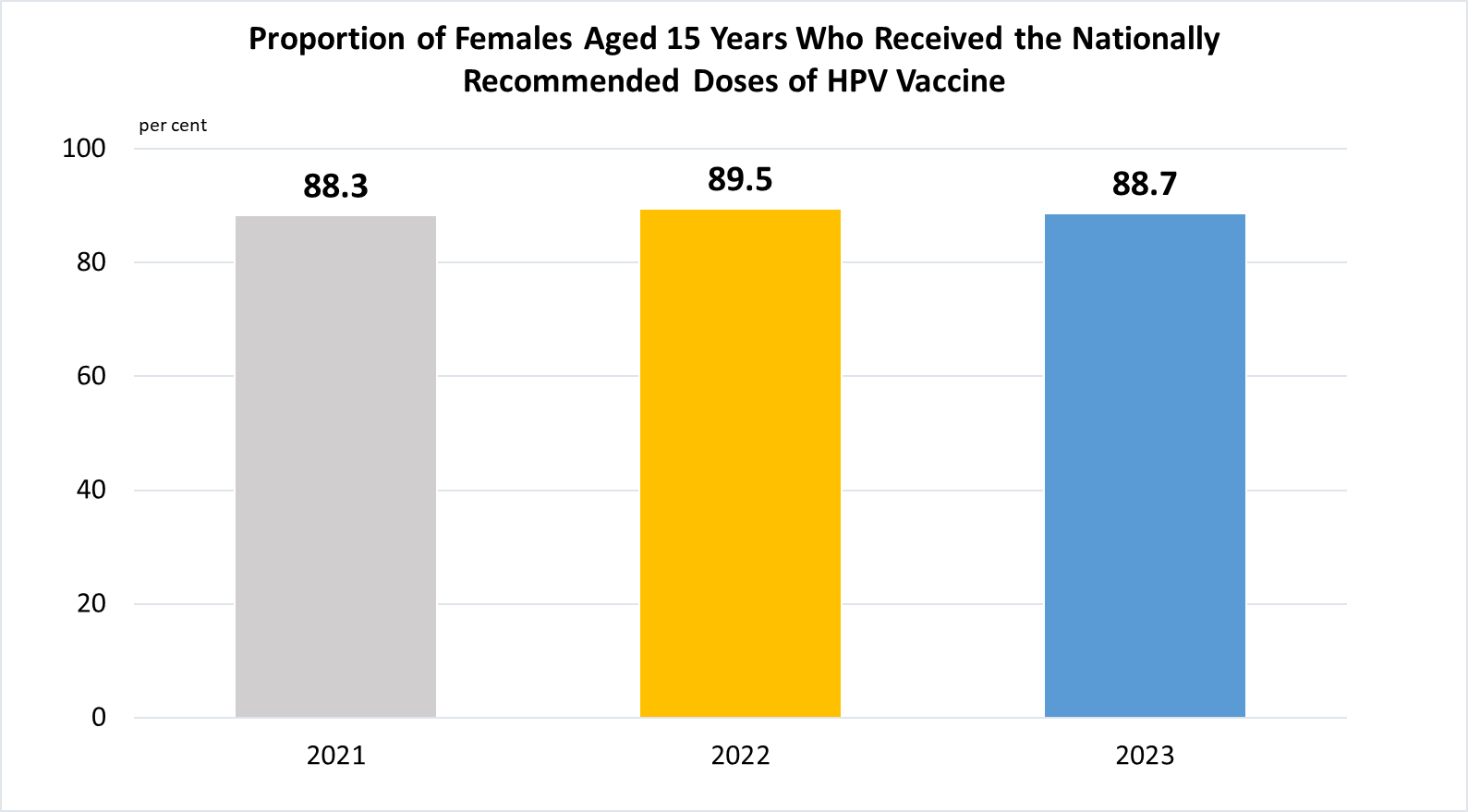
Data are based on Singapore residents (i.e. Singapore citizens and permanent residents) in the respective 15-year old birth cohort (e.g. data for 2023 refer to those born in 2008).
|
|
 |
Indicator 3.B.2 | Total net official development assistance to medical research and basic health sectors
|
Not applicable. Singapore does not receive Official Development Assistance.
|
|
 |
Increase Health Financing and Support Health Workforce in Developing Countries
Substantially increase health financing and the recruitment, development, training and retention of the health workforce in developing countries, especially in least developed countries and small island developing States.
|
Indicator 3.C.1 | Health worker density and distribution
|
(a)
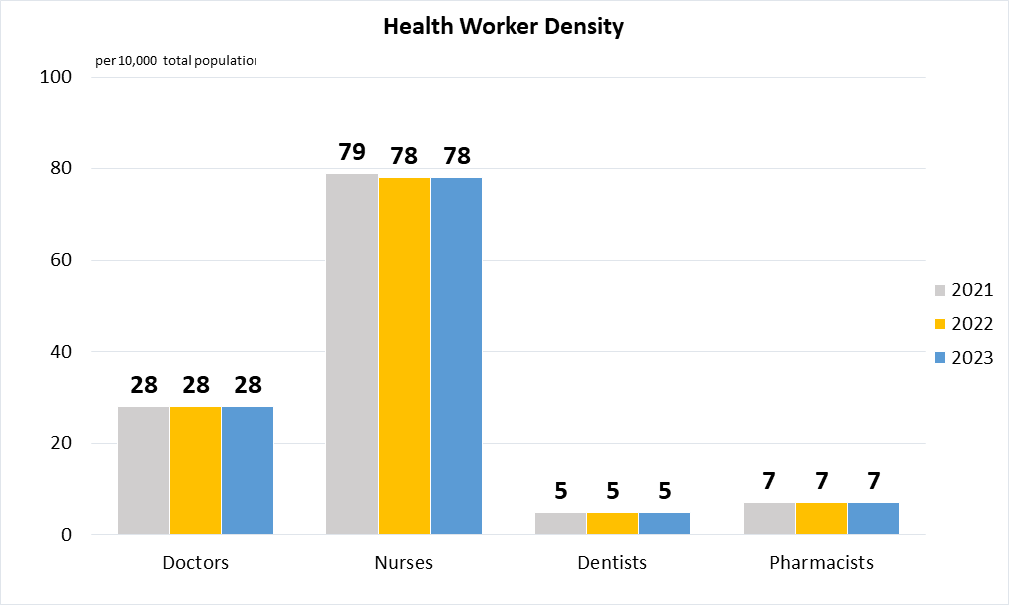
|
 |
 |
Improve Early Warning Systems for Global Health Risks
Strengthen the capacity of all countries, in particular developing countries, for early warning, risk reduction and management of national and global health risks.
|
Indicator 3.D.1 | International Health Regulations (IHR) capacity and health emergency preparedness
|
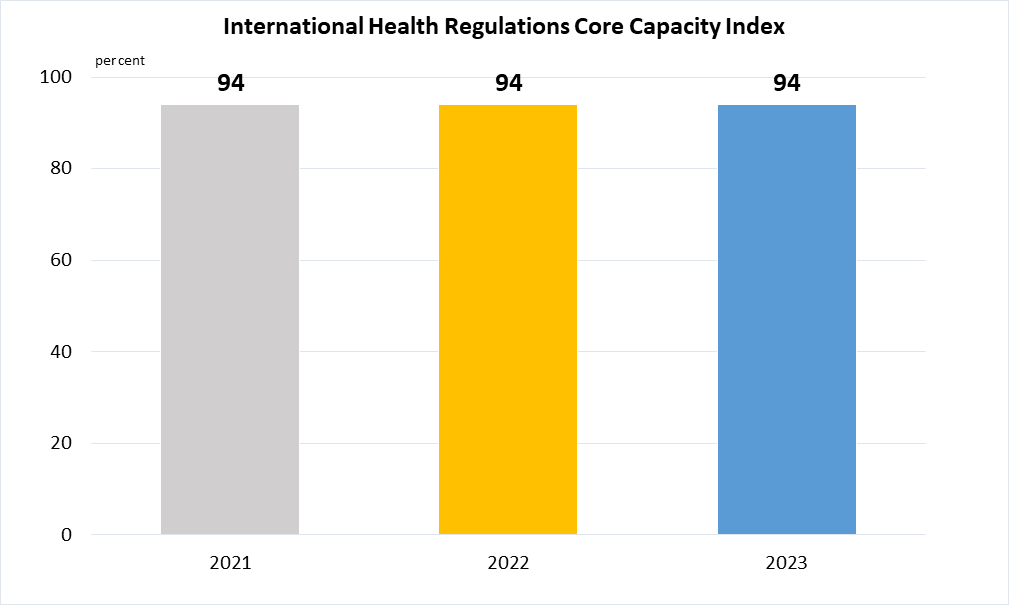
Data are available from 2018 onwards based on the State Party Self-Assessment Annual Reporting Tool (SPAR) developed by World Health Organisation (WHO), as part of WHO’s International Health Regulations (IHR) Monitoring and Evaluation Framework.
|
|
 |
Indicator 3.D.2 | Percentage of bloodstream infections due to selected antimicrobial-resistant organisms
|
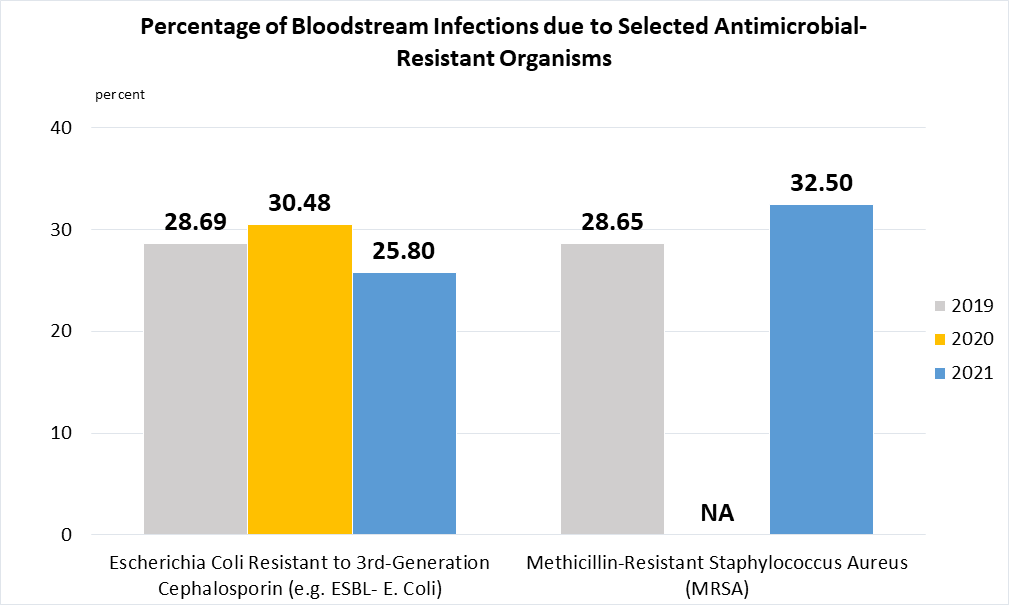
Data are taken from United Nations SDG Global Database.
Data are obtained from selected sentinel sites which may be updated from time to time.
|
 |