Sustainable Development Goals
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
Target 2.3 | Double the Productivity and Incomes of Small-Scale Food Producers
|
|
|
|
|
|
Targets and Indicators with Data Availability
Note: The data may be updated periodically as more information become available.
 |
Universal Access to Safe and Nutritious Food
By 2030, end hunger and ensure access by all people, in particular the poor and people in vulnerable situations, including infants, to safe, nutritious and sufficient food all year round.
|
Indicator 2.1.1 | Prevalence of undernourishment
|
Singapore takes an integrated approach to maintain our low levels of undernourishment, such as lowering the burden of undernourishment by ensuring access to quality healthcare and providing support for vulnerable families. For instance, as part of the interagency taskforce on Child and Maternal Health and Well-being, the Ministry of Health works with various government agencies and healthcare clusters to increase uptake of upstream preventive health services for children and enhance service integration and support for the children and families. The Health Promotion Board also collaborates with schools, parents and caregivers in supporting children in all aspects of their health, including adopting healthier diet and physical activity. Hence, Singapore does not routinely collect data on this indicator.
|
 |
Indicator 2.1.2 | Prevalence of moderate or severe food insecurity in the population, based on the Food Insecurity Experience Scale (FIES)
|
The burden of food insecurity is low in Singapore. Hence, Singapore does not routinely collect data on this indicator.
|
 |
 |
End All Forms of Malnutrition
By 2030, end all forms of malnutrition, including achieving, by 2025, the internationally agreed targets on stunting and wasting in children under 5 years of age, and address the nutritional needs of adolescent girls, pregnant and lactating women and older persons.
|
Indicator 2.2.1 | Prevalence of stunting (height for age <-2 standard deviation from the median of the World Health Organization (WHO) Child Growth Standards) among children under 5 years of age
|
Singapore takes an integrated approach to maintain our low levels of stunting, such as lowering the burden of stunting by ensuring access to quality healthcare and providing support for vulnerable families. For instance, as part of the interagency taskforce on Child and Maternal Health and Well-being, the Ministry of Health works with various government agencies and healthcare clusters to increase uptake of upstream preventive health services for children and enhance service integration and support for the children and families. The Health Promotion Board also collaborates with schools, parents and caregivers in supporting children in all aspects of their health, including adopting healthier diet and physical activity. Hence, Singapore does not routinely collect data on this indicator.
|
 |
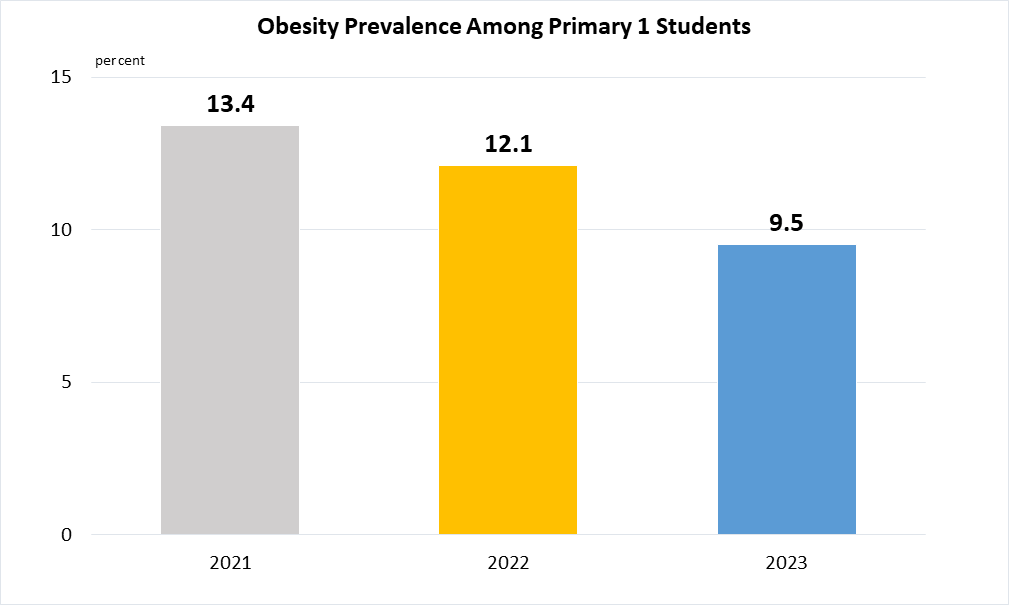
Indicator 2.2.2 | Prevalence of malnutrition (weight for height >+2 or <-2 standard deviation from the median of the WHO Child Growth Standards) among children under 5 years of age, by type (wasting and overweight)
|
(a)
Singapore takes an integrated approach to maintain our low levels of wasting, such as lowering the burden of wasting by ensuring access to quality healthcare and providing support for vulnerable families. For instance, as part of the interagency taskforce on Child and Maternal Health and Well-being, the Ministry of Health works with various government agencies and healthcare clusters to increase uptake of upstream preventive health services for children and enhance service integration and support for the children and families. The Health Promotion Board also collaborates with schools, parents and caregivers in supporting children in all aspects of their health, including adopting healthier diet and physical activity. Hence, Singapore does not routinely collect data on this indicator.
(b)
|
 |
Indicator 2.2.3 | Prevalence of anaemia in women aged 15 to 49 years, by pregnancy status (percentage)
|
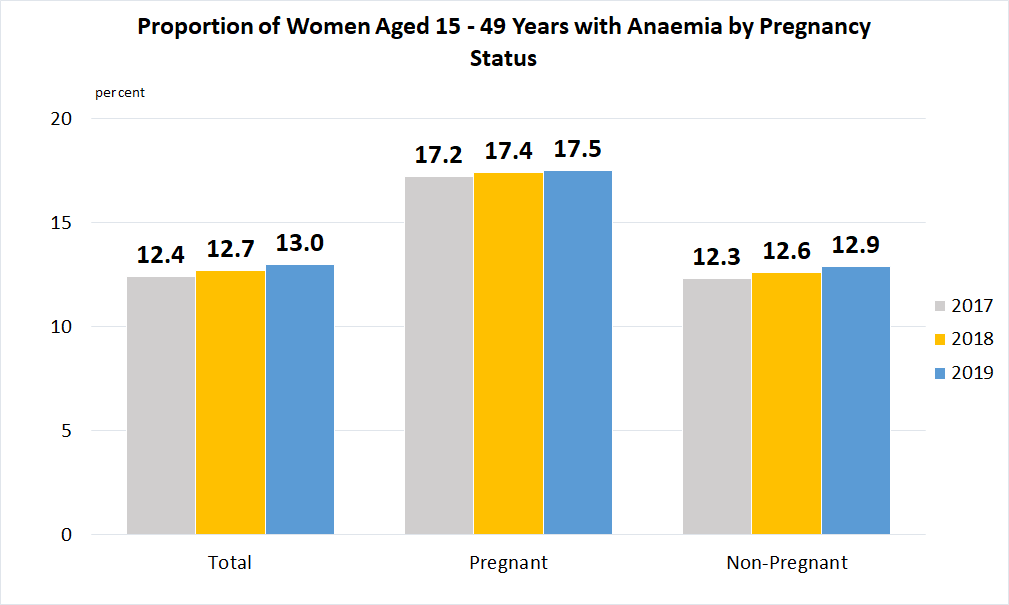
Data are taken from United Nations Global SDG Database.
|
 |
 |
Sustainable Food Production and Resilient Agricultural Practices
By 2030, ensure sustainable food production systems and implement resilient agricultural practices that increase productivity and production, that help maintain ecosystems, that strengthen capacity for adaptation to climate change, extreme weather, drought, flooding and other disasters and that progressively improve land and soil quality.
|
Indicator 2.4.1 | Proportion of agricultural area under productive and sustainable agriculture
|
Much of the land safeguarded for agriculture use is under active planning for long term comprehensive redevelopment. Meanwhile the Singapore Food Agency is concurrently launching annual land tenders for farm development to support and grow our local production sector. As such, the proportion of agriculture land currently put to productive use cannot be accurately determined.
|
 |
Maintain the Genetic Diversity in Food Production
By 2020, maintain the genetic diversity of seeds, cultivated plants and farmed and domesticated animals and their related wild species, including through soundly managed and diversified seed and plant banks at the national, regional and international levels, and promote access to and fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources and associated traditional knowledge, as internationally agreed.
|
Indicator 2.5.1 | Number of (a) plant and (b) animal genetic resources for food and agriculture secured in either medium- or long-term conservation facilities
|
The conservation of plant and animal genetic resources for food and agriculture (in either medium- or long-term conservation facilities) is not relevant for Singapore at this juncture.
|
 |
Indicator 2.5.2 | Proportion of local and transboundary breeds classified as being at risk of extinction
|
Singapore does not distinguish between local and non-local breeds for livestock given our relatively small agri- and aquaculture sector.
|
 |
Invest in Rural Infrastructure, Agricultural Research, Technology and Gene Banks
Increase investment, including through enhanced international cooperation, in rural infrastructure, agricultural research and extension services, technology development and plant and livestock gene banks in order to enhance agricultural productive capacity in developing countries, in particular least developed countries.
|
Indicator 2.A.1 | The agriculture orientation index for government expenditures
|
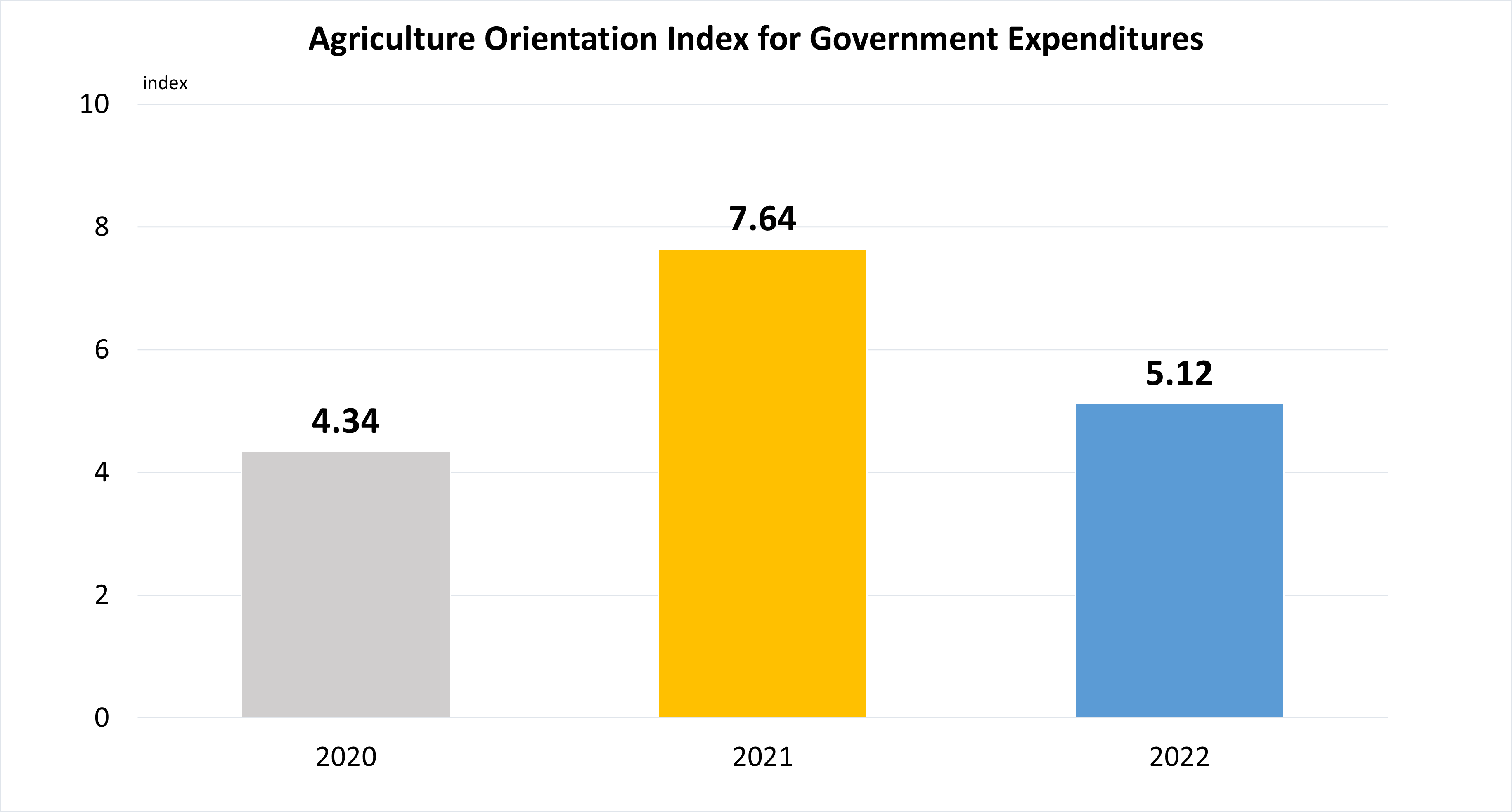
Data are based on the expenditures from budgetary central government.
|
 |
Indicator 2.A.2 | Total official flows (official development assistance plus other official flows) to the agriculture sector
|
Not applicable. Singapore does not receive Official Development Assistance.
|
|
 |
Prevent Agricultural Trade Restrictions, Market Distortions and Export Subsidies
Correct and prevent trade restrictions and distortions in world agricultural markets, including through the parallel elimination of all forms of agricultural export subsidies and all export measures with equivalent effect, in accordance with the mandate of the Doha Development Round.
|
Indicator 2.B.1 | Agricultural export subsidies
|
Amount of agricultural export subsidies is 0 as Singapore does not provide export subsidies for the agriculture sector.
|
|
 |
Ensure Stable Food Commodity Markets and Timely Access to Information
Adopt measures to ensure the proper functioning of food commodity markets and their derivatives and facilitate timely access to market information, including on food reserves, in order to help limit extreme food price volatility.
|
Indicator 2.C.1 | Indicator of food price anomalies
|
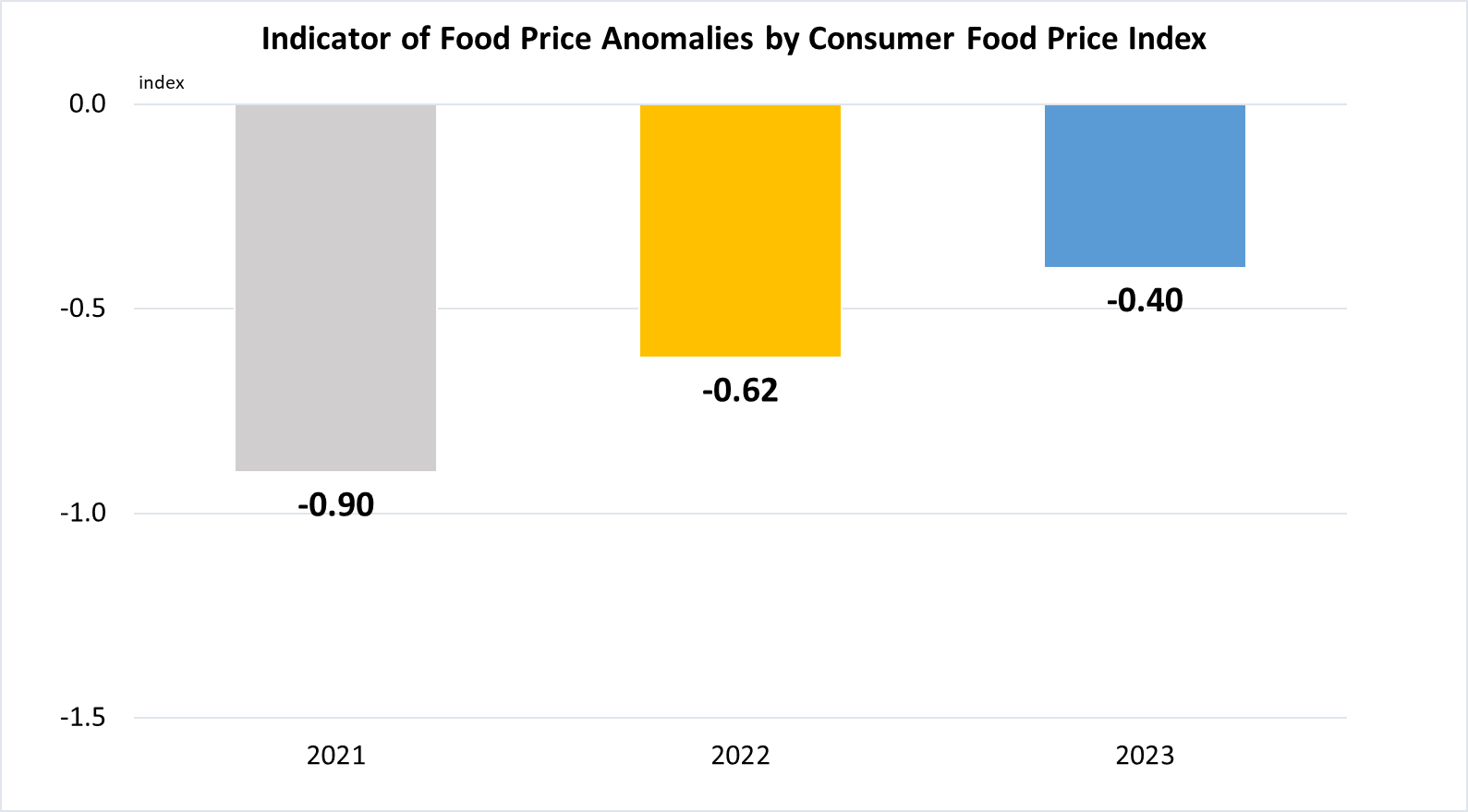
Data are taken from United Nations Global SDG Database.
Data refer to the twelve month average of the monthly price anomalies and are defined as (i) abnormally high if the Indicator of Food Price Anomalies (IFPA) >= 1; (ii) moderately high if 0.5 =< IFPA< 1; and (iii) normal if -0.5 =< IFPA < 0.5.
|
 |