Sustainable Development Goals
Targets and Indicators with Data Availability
Note: The data may be updated periodically as more information become available.
 |
Implement the 10-year Sustainable Consumption and Production Framework
Implement the 10-Year Framework of Programmes on Sustainable Consumption and Production Patterns, all countries taking action, with developed countries taking the lead, taking into account the development and capabilities of developing countries.
|
Indicator 12.1.1 | Number of countries developing, adopting or implementing policy instruments aimed at supporting the shift to sustainable consumption and production
|
In 2019, Singapore launched the Zero Waste Masterplan, which outlines our circular economy approach to encourage sustainable consumption and production. Singapore also introduced the Resource Sustainability Act that will put in place a systems-level approach that mandates key responsibilities to enable re-use and recycling nation-wide. Sustainable development has been the cornerstone of Singapore’s continued progress since our independence and will continue to be an ongoing journey.
|
|
 |
 |
Sustainable Management and Use of Natural Resources
By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
|
Indicator 12.2.1 | Material footprint, material footprint per capita, and material footprint per GDP
Indicator 12.2.2 | Domestic material consumption, domestic material consumption per capita, and domestic material consumption per GDP
 |
Halve Global Per Capita Food Waste
By 2030, halve per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels and reduce food losses along production and supply chains, including post-harvest losses.
|
Indicator 12.3.1 | (a) Food loss index and (b) food waste index
|
(b)
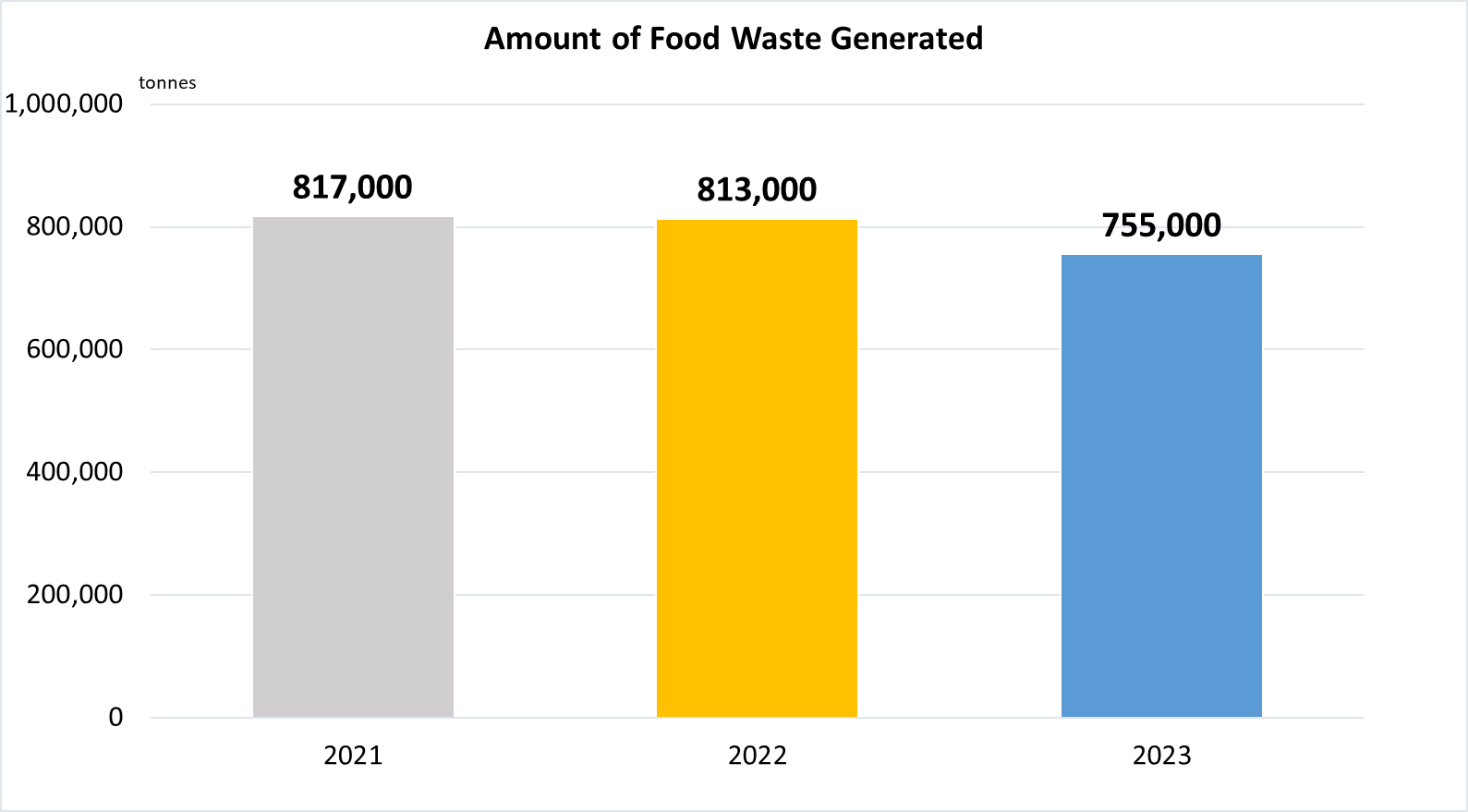
Food waste generated includes food waste disposed of and food waste recycled.
|
|
 |
Responsible Management of Chemicals and Waste
By 2020, achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes throughout their life cycle, in accordance with agreed international frameworks, and significantly reduce their release to air, water and soil in order to minimize their adverse impacts on human health and the environment.
|
Indicator 12.4.1 | Number of parties to international multilateral environmental agreements on hazardous waste, and other chemicals that meet their commitments and obligations in transmitting information as required by each relevant agreement
|
As a party to several Multilateral Environmental Agreements (MEAs) on hazardous chemicals and waste, Singapore has put in place measures to meet its obligations.
|
|
 |
Indicator 12.4.2 | (a) Hazardous waste generated per capita; and (b) Proportion of hazardous waste treated, by type of treatment
|
(a)
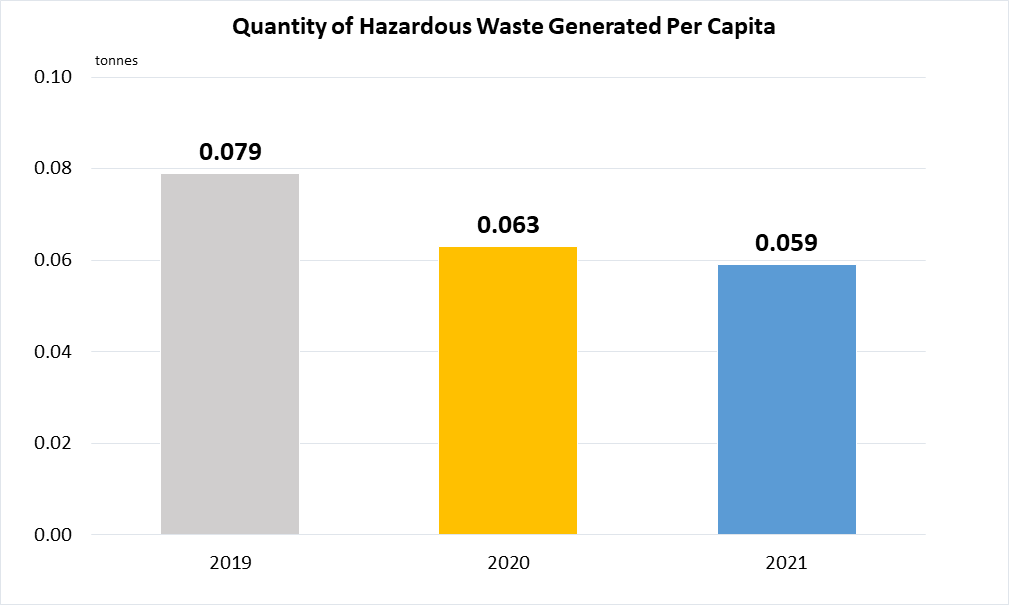
Data are based on records of hazardous waste being collected and treated.
(b) Since data are based on records of hazardous waste being collected and treated, the total proportion of generated hazardous wastes that are treated in Singapore is 100%.
|
|
 |
 |
Substantially Reduce Waste Generation
By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse.
|
Indicator 12.5.1 | National recycling rate, tons of material recycled
|
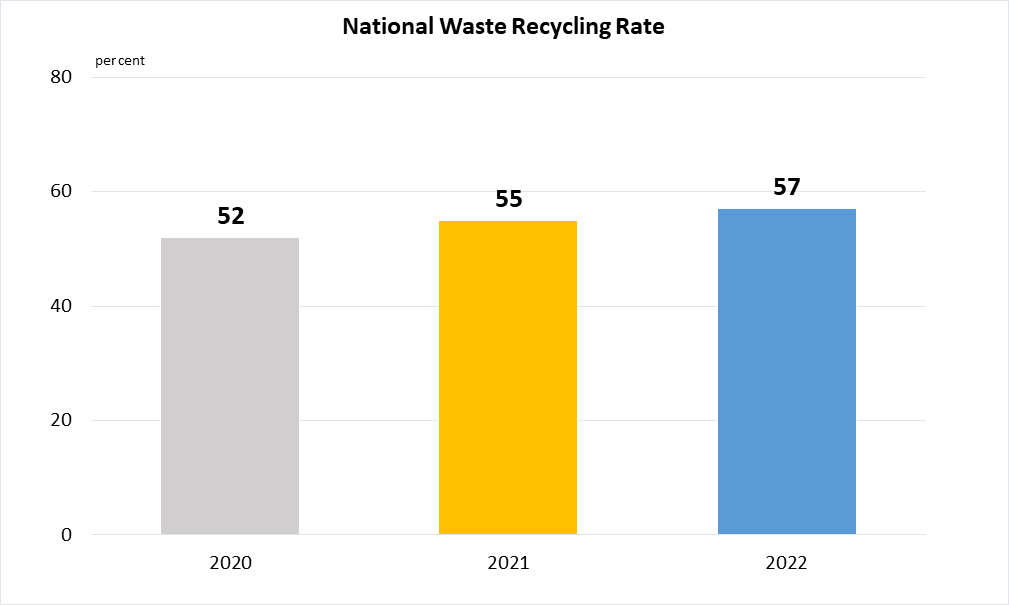
Data refer to proportion of total solid waste recycled over total solid waste generated by Singapore.
|
|
 |
 |
Encourage Companies to Adopt Sustainable Practices and Sustainability Reporting
Encourage companies, especially large and transnational companies, to adopt sustainable practices and to integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycle..
|
Indicator 12.6.1 | Number of companies publishing sustainability reports
|
(a)
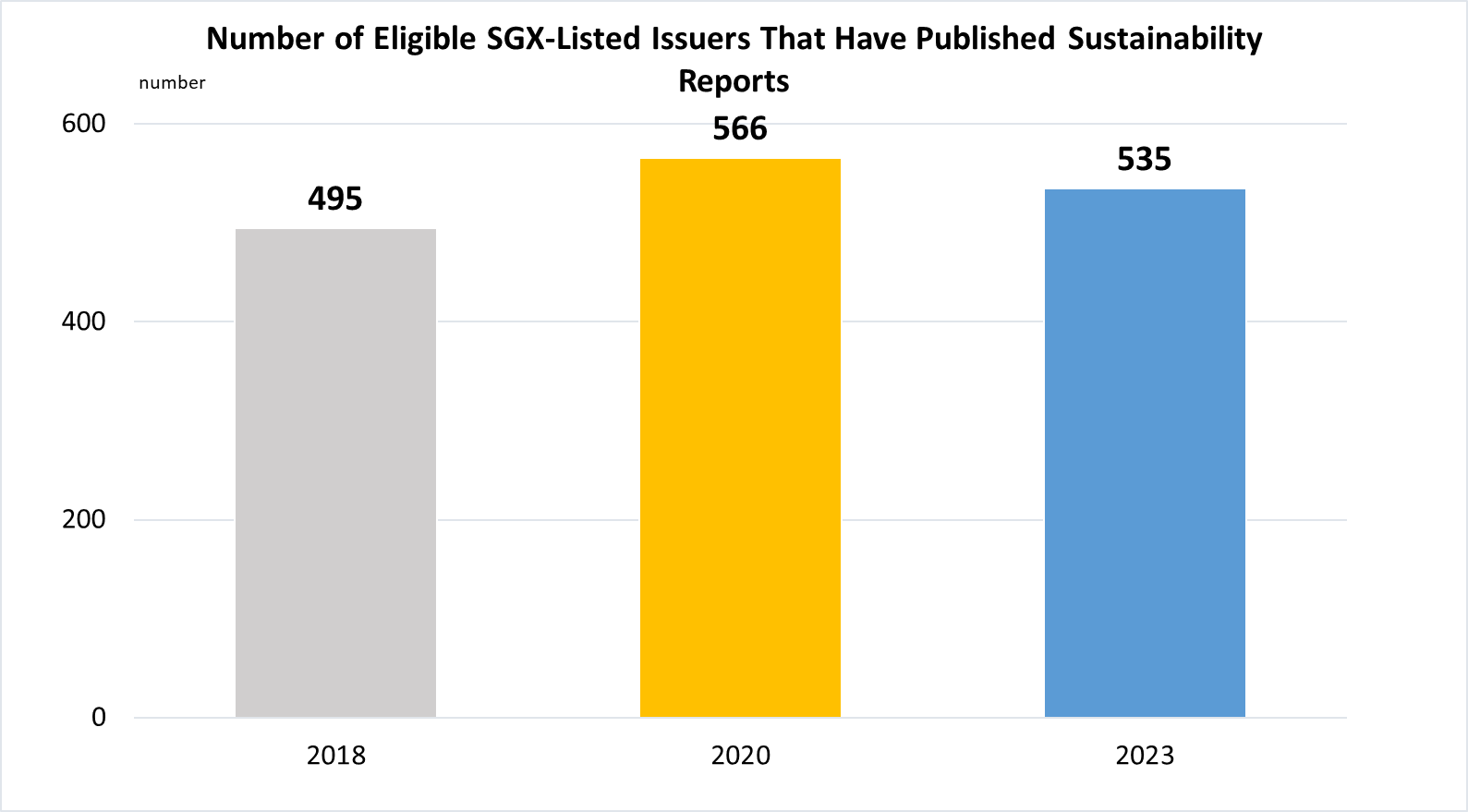
Data are taken from the Sustainability Reporting joint reviews published by Singapore Exchange (SGX) and the Centre for Governance and Sustainability (CGS) at National University of Singapore (NUS) Business School. Data are based on the assessment cut-off years for the reference periods.
(b)
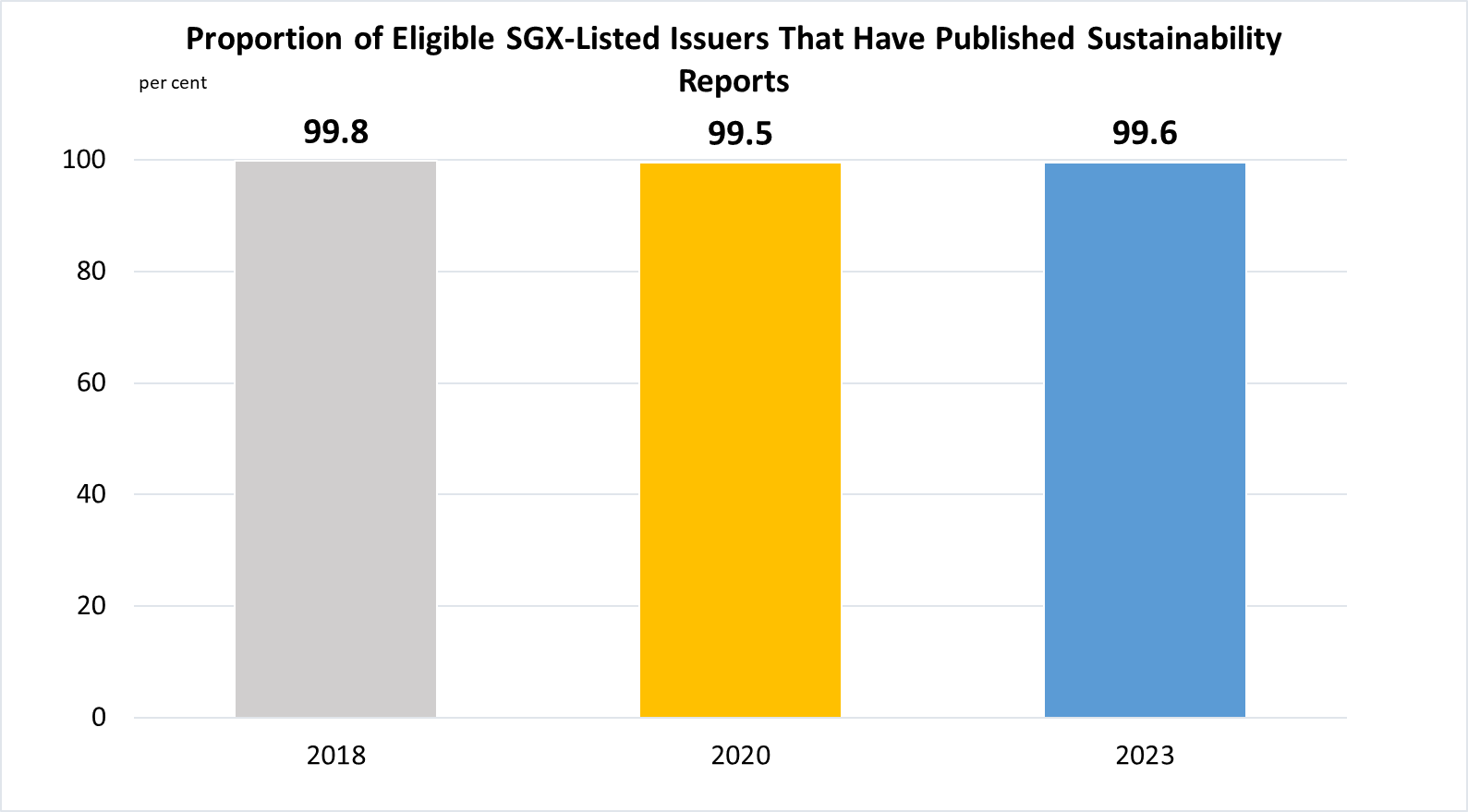
Data are taken from the Sustainability Reporting joint reviews published by Singapore Exchange (SGX) and the Centre for Governance and Sustainability (CGS) at National University of Singapore (NUS) Business School. Data are based on the assessment cut-off years for the reference periods.
|
|
 |
Promote Sustainable Public Procurement Practices
Promote public procurement practices that are sustainable, in accordance with national policies and priorities.
|
Indicator 12.7.1 | Number of countries implementing sustainable public procurement policies and action plans
|
Singapore has implemented sustainable public procurement policies and action plans since 2007.
|
|
 |
 |
Promote Universal Understanding of Sustainable Lifestyles
By 2030, ensure that people everywhere have the relevant information and awareness for sustainable development and lifestyles in harmony with nature.
|
Indicator 12.8.1 | Extent to which (i) global citizenship education and (ii) education for sustainable development are mainstreamed in (a) national education policies; (b) curricula; (c) teacher education; and (d) student assessment
|
Since 2021, the Ministry of Education's Eco Stewardship Programme (ESP) has been implemented in all schools to nurture students to be environmental stewards. As the education pillar of the Singapore Green Plan 2030, the ESP integrates sustainability into curricula across levels and subjects, including in the Humanities, Sciences, Food and Consumer Education and Character and Citizenship Education. This is complemented by school-based initiatives for students to further engage in learning experiences related to sustainability. Schools' campuses are also progressively enhanced with sustainability features that help connect students' lived experiences with their learning. Sustainability is featured in teachers' professional learning roadmap, which includes relevant professional development opportunities such as workshops, learning journeys and work attachments.
|
|
 |
Support Developing Countries' Scientific and Technological Capacity for Sustainable Consumption and Production
Support developing countries to strengthen their scientific and technological capacity to move towards more sustainable patterns of consumption and production.
|
Indicator 12.A.1 | Installed renewable energy-generating capacity in developing and developed countries (in Watts per capita)
 |
Develop and Implement Tools to Monitor Sustainable Tourism
Develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products.
|
Indicator 12.B.1 | Implementation of standard accounting tools to monitor the economic and environmental aspects of tourism sustainability
|
Singapore has compiled 4 Tourism Satellite Account (TSA) tables for reference year 2015 to monitor the economic aspects of tourism.
|
|
 |
 |
Remove Market Distortions that Encourage Wasteful Consumption
Rationalize inefficient fossil-fuel subsidies that encourage wasteful consumption by removing market distortions, in accordance with national circumstances, including by restructuring taxation and phasing out those harmful subsidies, where they exist, to reflect their environmental impacts, taking fully into account the specific needs and conditions of developing countries and minimizing the possible adverse impacts on their development in a manner that protects the poor and the affected communities.
|
Indicator 12.C.1 | Amount of fossil-fuel subsidies (production and consumption) per unit of GDP
|
Amount of fossil-fuel subsidies (production and consumption) per unit of GDP is 0 since no subsidies are given for the power and gas sectors.
|
|