Sustainable Development Goals
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
Target 17.4 | Assist Developing Countries in Attaining Debt Sustainability
|
-
Target 17.14 | Enhance Policy Coherence for Sustainable Development
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
Target 17.7 | Promote Sustainable Technologies to Developing Countries
|
-
Target 17.17 | Encourage Effective Partnerships
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Targets and Indicators with Data Availability
Note: The data may be updated periodically as more information become available.
 |
Mobilize Resources to Improve Domestic Revenue Collection
Strengthen domestic resource mobilization, including through international support to developing countries, to improve domestic capacity for tax and other revenue Collection.
|
Indicator 17.1.1 | Total government revenue as a proportion of GDP, by source
|
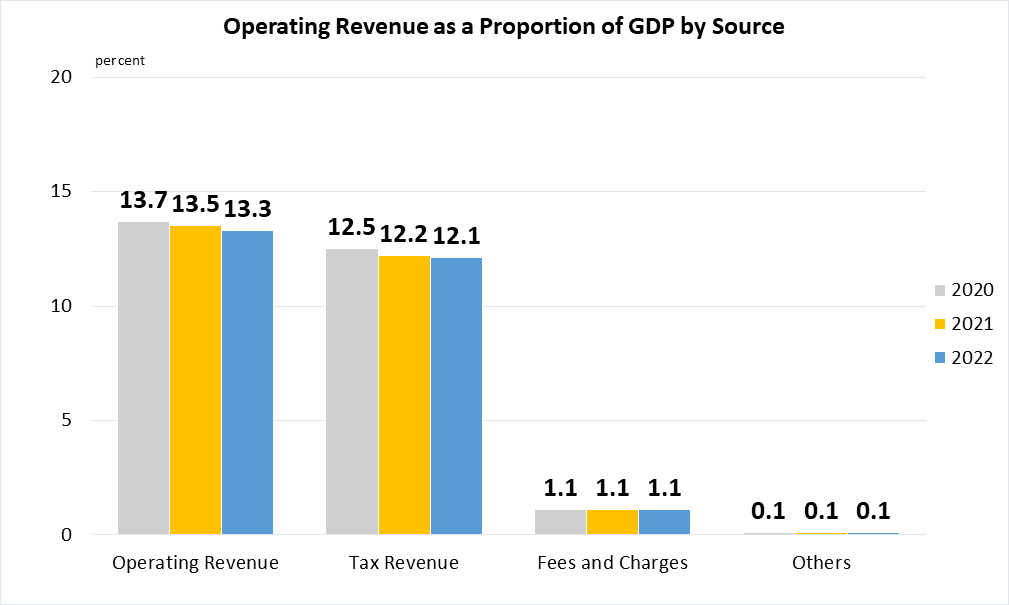
Operating Revenue refers to government receipts credited to the Consolidated Revenue Account and Development Fund Account, excluding investment and interest income, and capital receipts (lumpy and less regular in timing). Sources of Operating Revenue comprise of Tax Revenue, Fees and Charges, and Others. The main components of Tax Revenue are Corporate Income Tax, Personal Income Tax, and Goods and Services Tax.
Fees and Charges includes Vehicle Quota Premiums, which is highly volatile.
Note: Data for Tax Revenue, Fees and Charges and Others may not add up to Operating Revenue due to rounding. Data for latest available year are preliminary.
|
 |
Indicator 17.1.2 | Proportion of domestic budget funded by domestic taxes
|
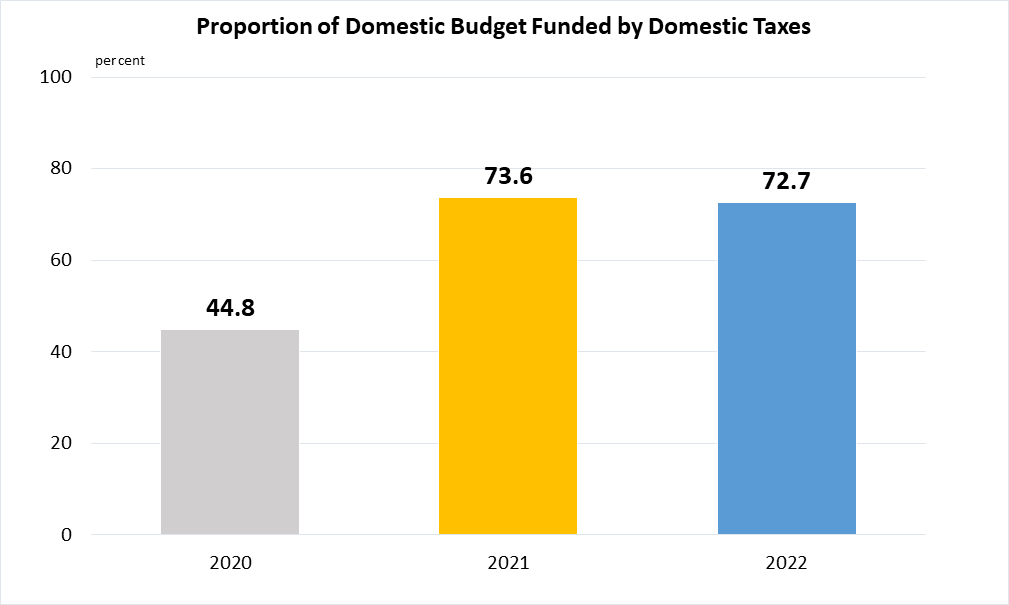
Singapore's budget is funded from both Operating Revenue (comprising taxes and fees and charges) and the investment returns from our reserves (i.e. Net Investment Returns Contribution).
|
 |
 |
Implement All Development Assistance Commitments
Developed countries to implement fully their official development assistance commitments, including the commitment by many developed countries to achieve the target of 0.7 per cent of gross national income for official development assistance (ODA/GNI) to developing countries and 0.15 to 0.20 per cent of ODA/GNI to least developed countries; ODA providers are encouraged to consider setting a target to provide at least 0.20 per cent of ODA/GNI to least developed countries.
|
Indicator 17.2.1 | Net official development assistance, total and to least developed countries, as a proportion of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) Development Assistance Committee donors’ gross national income (GNI)
|
Not applicable. Singapore does not provide Official Development Assistance. Singapore provides capacity building for other developing countries under the Singapore Cooperation Programme, which aims to help them achieve the SDGs.
|
|
 |
Mobilize Financial Resources for Developing Countries
Mobilize additional financial resources for developing countries from multiple sources.
|
Indicator 17.3.1 | Additional financial resources mobilized for developing countries from multiple sources
|
Not applicable. Singapore does not receive Official Development Assistance.
|
|
 |
Invest in Least Developed Countries
Adopt and implement investment promotion regimes for least developed countries.
|
Indicator 17.5.1 | Number of countries that adopt and implement investment promotion regimes for developing countries, including the least developed countries
|
Not applicable. Singapore does not adopt and implement investment promotion regimes for other developing countries.
|
|
 |
Knowledge Sharing and Cooperation for Access to Science, Technology and Innovation
Enhance North-South, South-South and triangular regional and international cooperation on and access to science, technology and innovation and enhance knowledge-sharing on mutually agreed terms, including through improved coordination among existing mechanisms, in particular at the United Nations level, and through a global technology facilitation mechanism.
|
Indicator 17.6.1 | Fixed broadband subscriptions per 100 inhabitants, by speed
 |
Strengthen the Science, Technology and Innovation Capacity for Least Developed Countries
Fully operationalise the technology bank and science, technology and innovation capacity-building mechanism for least developed countries by 2017 and enhance the use of enabling technology, in particular information and communications technology.
|
Indicator 17.8.1 | Proportion of individuals using the Internet
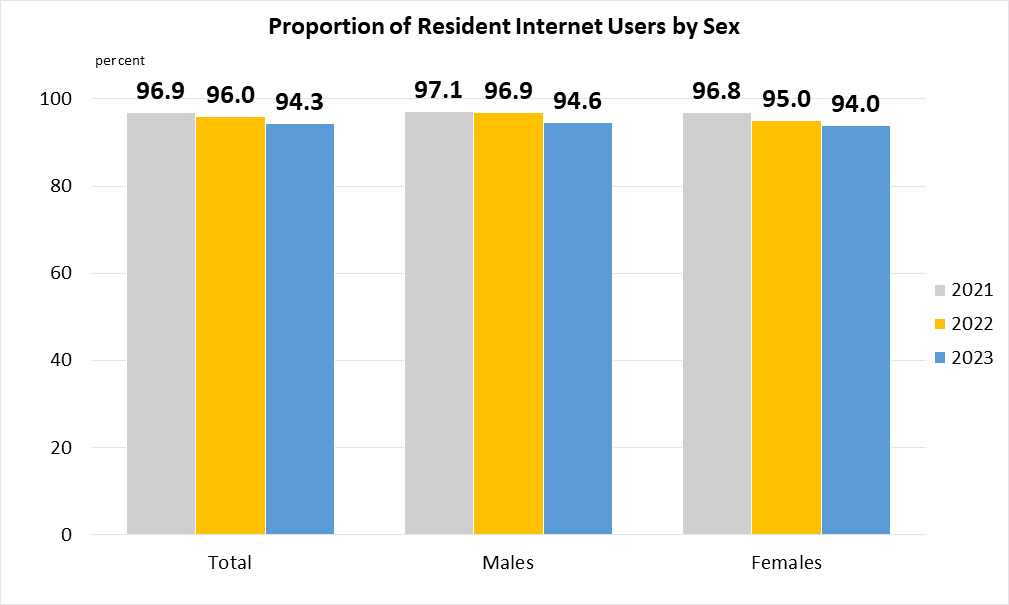
Data from 2020 onwards are based on Singapore residents (i.e. Singapore citizens and permanent residents) aged 16-74 years. Data prior to 2020 are based on residents of all age groups.
|
 |
 |
Enhance SDG Capacity in Developing Countries
Enhance international support for implementing effective and targeted capacity-building in developing countries to support national plans to implement all the Sustainable Development Goals, including through North-South, South-South and triangular cooperation.
|
Indicator 17.9.1 | Dollar value of official development assistance committed to developing countries
|
Not applicable. Singapore neither receives nor provides Official Development Assistance. Singapore provides capacity building for other developing countries under the Singapore Cooperation Programme, which aims to help them achieve the SDGs.
|
|
 |
Promote a Universal Trading System under the WTO
Promote a universal, rules-based, open, non-discriminatory and equitable multilateral trading system under the World Trade Organization, including through the conclusion of negotiations under its Doha Development Agenda.
|
Indicator 17.10.1 | Worldwide weighted tariff-average
Data are taken from United Nations SDG Global Database.
|
 |
Increase the Exports of Developing Countries
Significantly increase the exports of developing countries, in particular with a view to doubling the least developed countries’ share of global exports by 2020.
|
Indicator 17.11.1 | Developing countries’ and least developed countries’ share of global exports
|
(a)
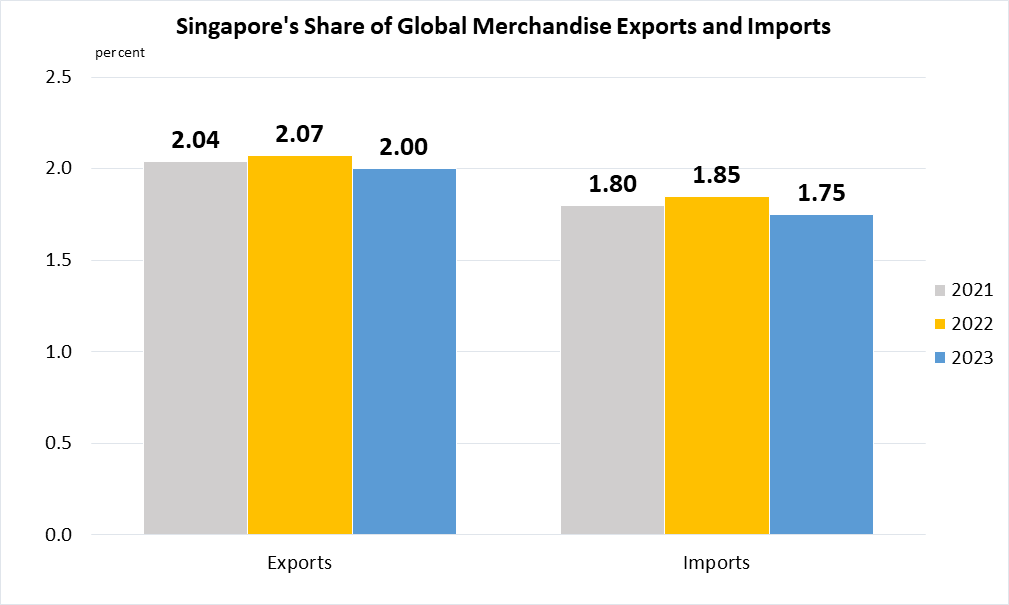
Data are taken from United Nations SDG Global Database.
(b)
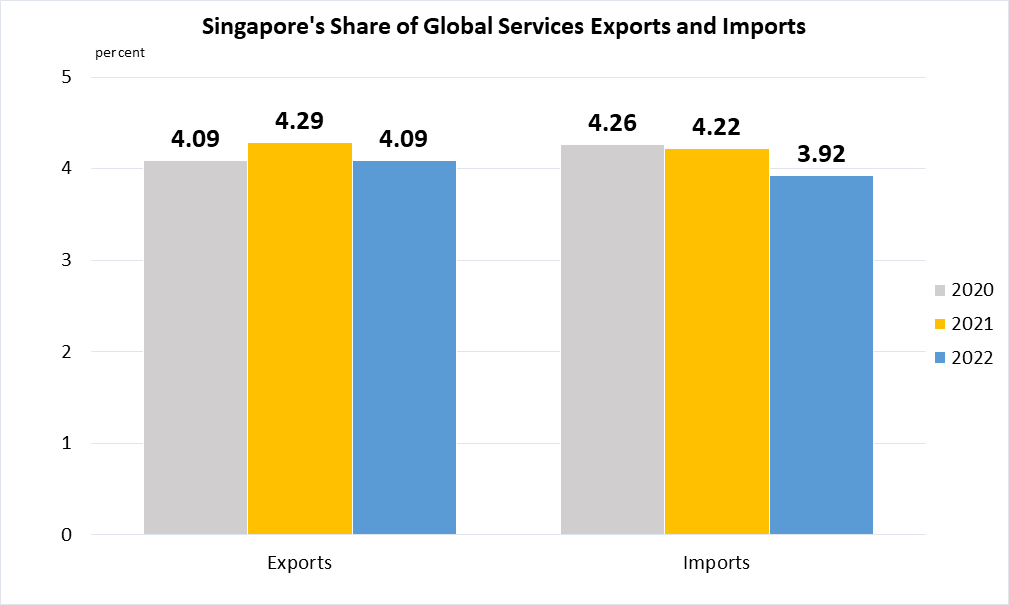
Data are taken from United Nations Global SDG database.
|
|
 |
Remove Trade Barriers for Least Developed Countries
Realize timely implementation of duty-free and quota-free market access on a lasting basis for all least developed countries, consistent with World Trade Organization decisions, including by ensuring that preferential rules of origin applicable to imports from least developed countries are transparent and simple, and contribute to facilitating market access.
|
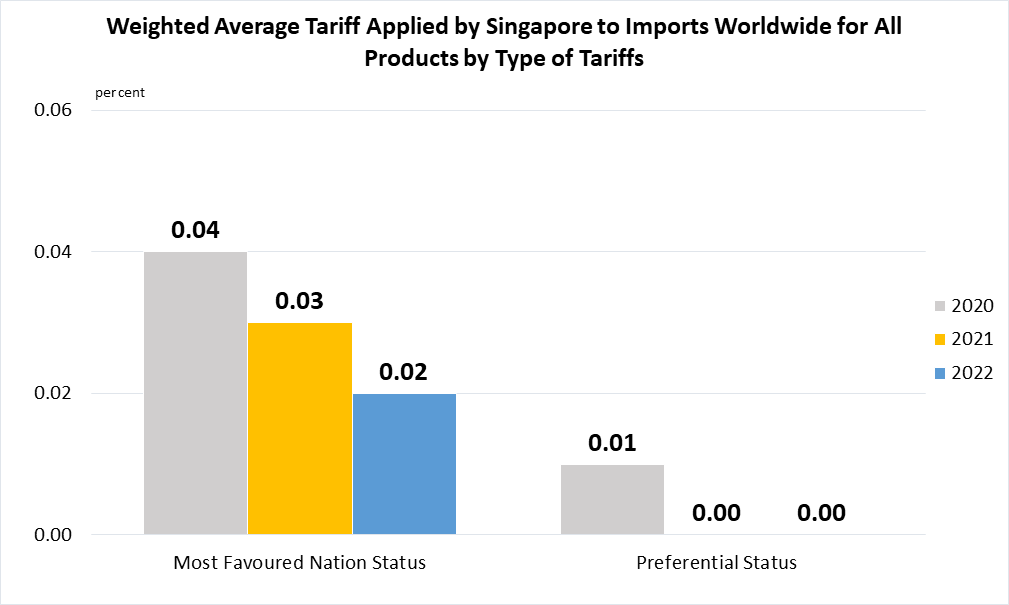
Indicator 17.12.1 | Weighted average tariffs faced by developing countries, least developed countries and small island developing States
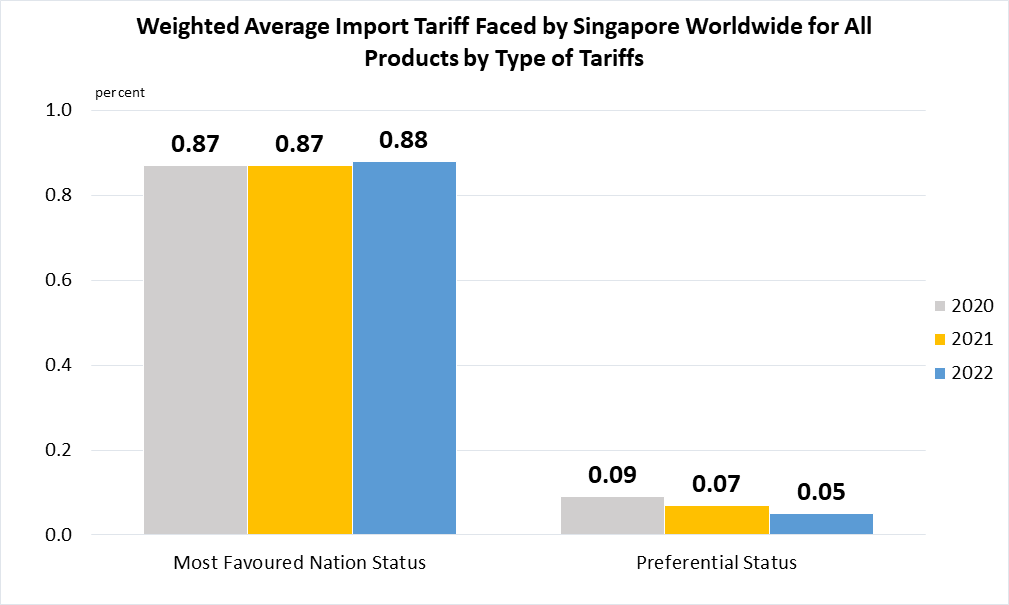
Data are taken from United Nations SDG Global Database.
|
 |
Enhance Global Macroeconomic Stability
Enhance global macroeconomic stability, including through policy coordination and policy coherence.
|
Indicator 17.13.1 | Macroeconomic Dashboard
|
Key macroeconomic indicators covering the external, financial, fiscal, and real sectors are compiled and monitored regularly to facilitate informed and evidence-based policymaking.
|
|
 |
 |
Respect National leadership to Implement Policies for the Sustainable Development Goals
Respect each country’s policy space and leadership to establish and implement policies for poverty eradication and sustainable Development.
|
Indicator 17.15.1 | Extent of use of country-owned results frameworks and planning tools by providers of development cooperation
|
Not applicable. Singapore does not receive development cooperation support. Singapore provides capacity building for other developing countries under the Singapore Cooperation Programme, which aims to help them achieve the SDGs.
|
|
 |
Enhance the Global Partnership for Sustainable Development
Enhance the Global Partnership for Sustainable Development, complemented by multi-stakeholder partnerships that mobilize and share knowledge, expertise, technology and financial resources, to support the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals in all countries, in particular developing countries.
|
Indicator 17.16.1 | Number of countries reporting progress in multi-stakeholder development effectiveness monitoring frameworks that support the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals
|
Not applicable. Singapore does not report to multi-stakeholder development effectiveness monitoring frameworks.
|
|
 |
Enhance Availability of Reliable Data
By 2020, enhance capacity-building support to developing countries, including for least developed countries and small island developing States, to increase significantly the availability of high-quality, timely and reliable data disaggregated by income, gender, age, race, ethnicity, migratory status, disability, geographic location and other characteristics relevant in national contexts.
|
Indicator 17.18.1 | Statistical capacity indicators
|
(a)
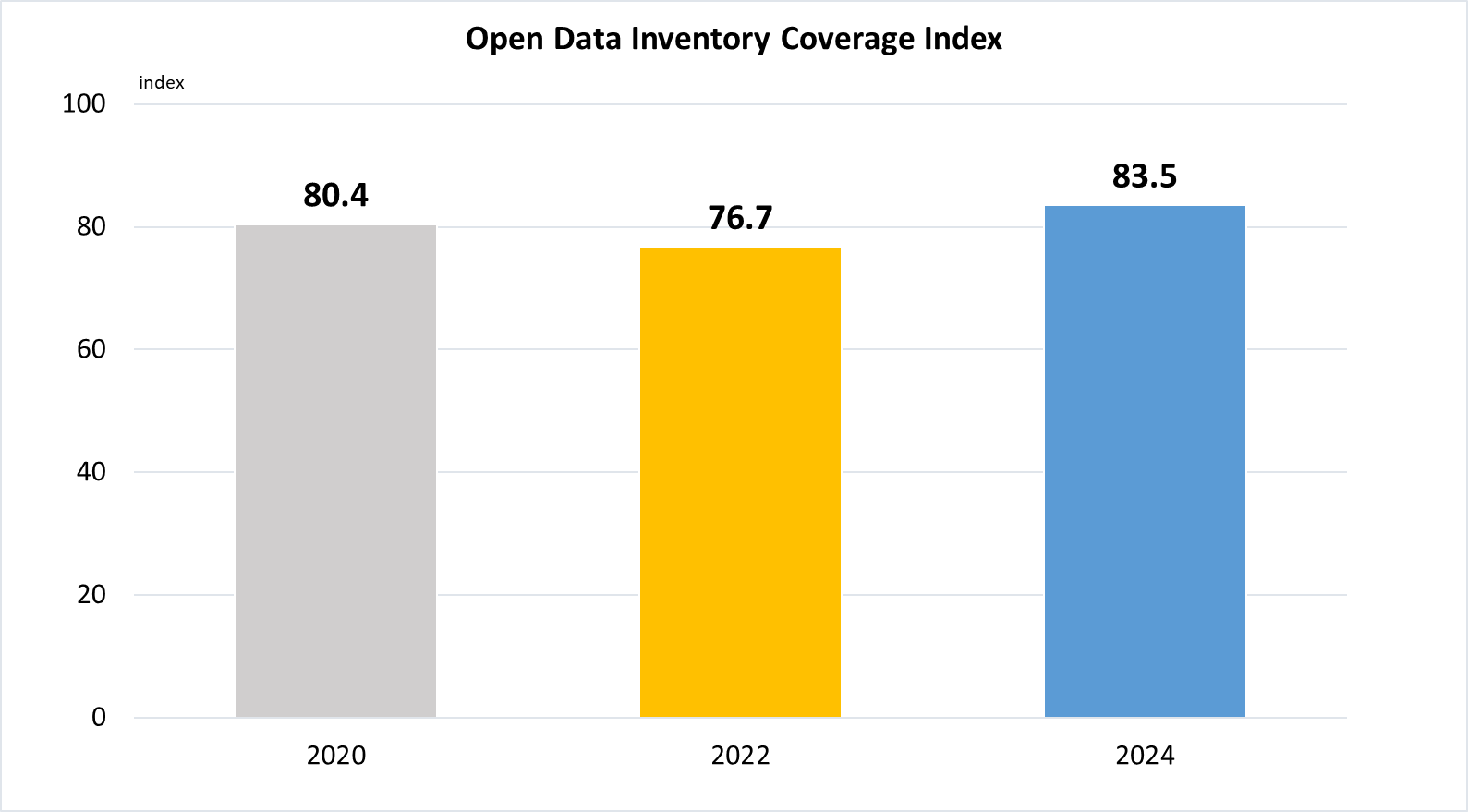
Data are taken from United Nations SDG Global Database.
(b)
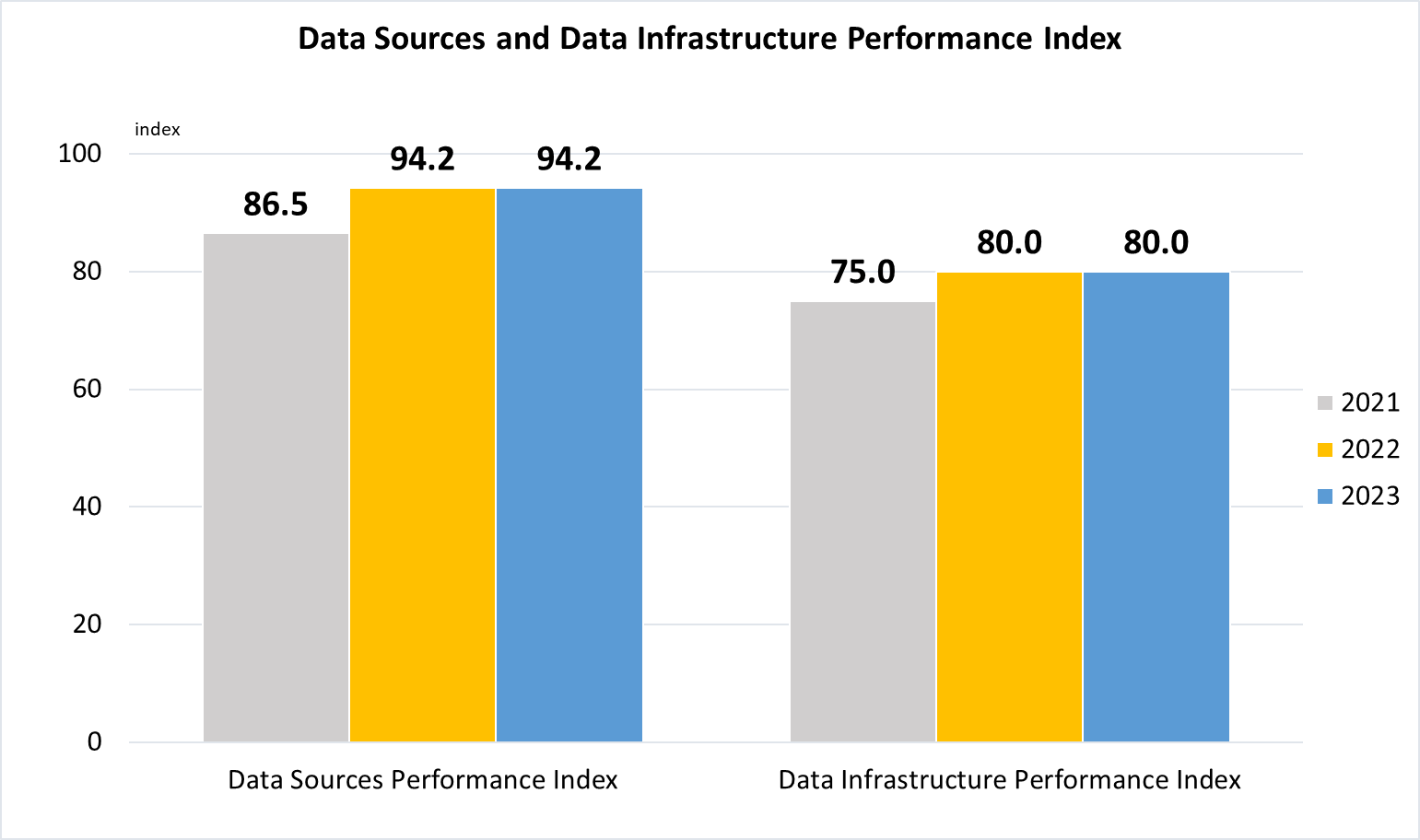
Data are taken from United Nations SDG Global Database.
|
 |
Indicator 17.18.2 | Number of countries that have national statistical legislation that complies with the Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics
|
Singapore has a national statistical legislation that complies with the United Nations Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics.
|
|
 |
Indicator 17.18.3 | Number of countries with a national statistical plan that is fully funded and under implementation, by source of funding
|
Singapore has a national statistical plan that is fully funded via the Budget and under implementation.
|
 |
 |
Further Develop Measurements of Progress
By 2030, build on existing initiatives to develop measurements of progress on sustainable development that complement gross domestic product, and support statistical capacity-building in developing countries.
|
Indicator 17.19.1 | Dollar value of all resources made available to strengthen statistical capacity in developing countries
|
Not applicable. Singapore neither receives nor provides Official Development Assistance. Singapore provides capacity building for other developing countries under the Singapore Cooperation Programme, which aims to help them achieve the SDGs.
|
Indicator 17.19.2 | Proportion of countries that (a) have conducted at least one population and housing census in the last 10 years; and (b) have achieved 100 per cent birth registration and 80 per cent death registration
|
(a) Singapore conducts the Census of Population once every 10 years, during the years ending with '0'. The latest was conducted in 2020.
(b) Singapore is estimated to have achieved nearly 100% local birth registration and at least 80% local death registration.
|
 |